Engine, clutch and transmission 2*15
nft i
i
■ A
1
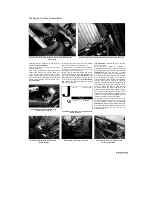
8.12b Measure the height of the camshaft
lobes with a micrometer
8.13 Measuring camshaft runout
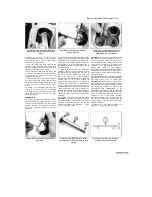
8.15 Lay a strip of Plastigauge across
each bearing journal, parallel with the
camshaft centreline
with a micrometer
(see illustration)
and
compare the results to the minimum lobe height
listed in this Chapter's Specifications. If damage
is noted or wear is excessive, the camshaft must
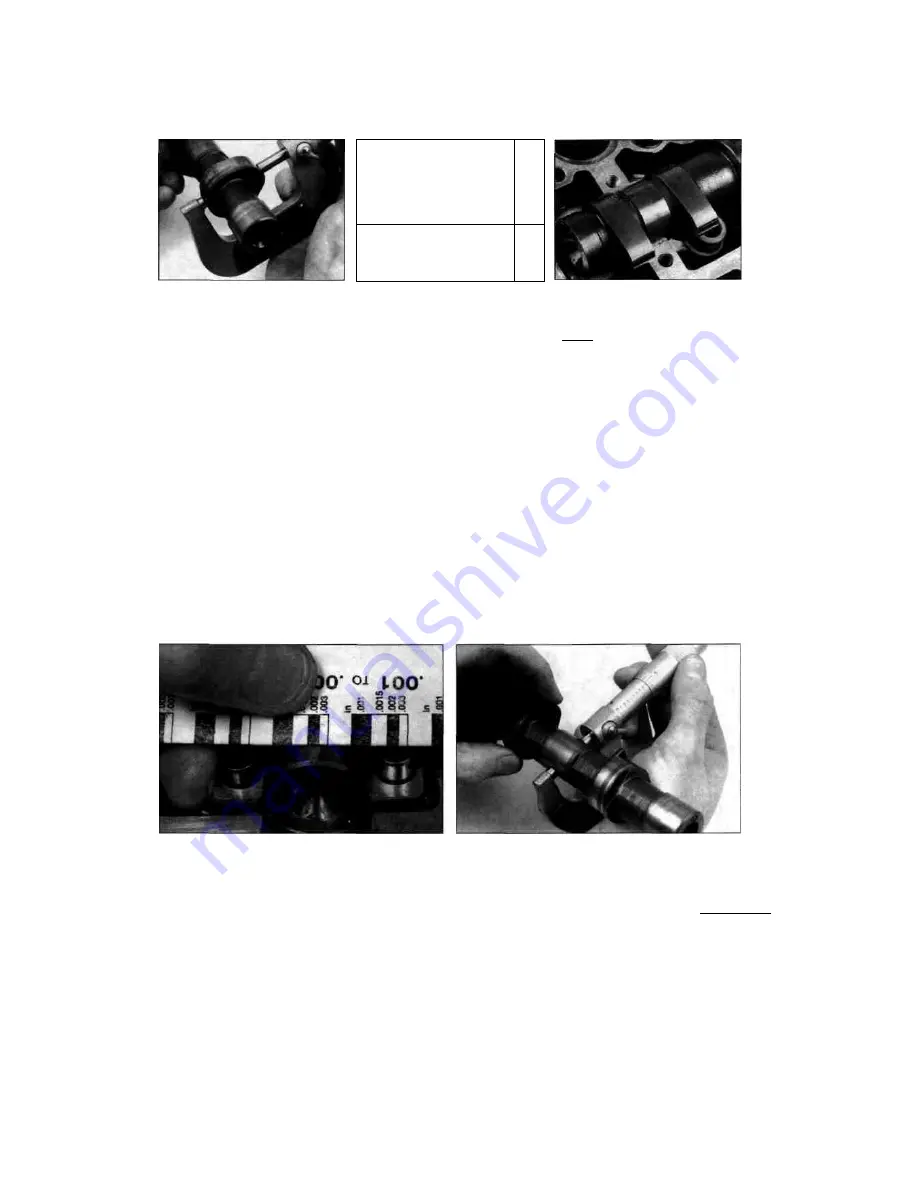
be renewed. Also, be sure to check the condition
of the followers. 13 Check the amount of
camshaft runout by supporting each end of the
camshaft on V-blocks, and measuring any runout
using a dial gauge
(see illustration).
If the
runout exceeds the specified limit the camshaft
must be renewed.
Refer to Tools and Workshop Tips
in the Reference section for
details of how to read a
micrometer and dial gauge.
14 Next, check the camshaft bearing oil
clearances. Check each camshaft in turn rather
than at the same time. Clean the camshaft, the
bearing surfaces in the cylinder head and
camshaft holders with a clean lint-free cloth, then
lay the camshaft in place in the cylinder head.
15 Cut some strips of Plastigauge and lay one
piece on each bearing journal, parallel with the
camshaft centreline
(see
illustration).
Make sure the camshaft holder
dowels are installed. Lay the holders in their
correct place in the cylinder head (see Step 8)
(see illustration 8.26a).
Make sure the arrow on
each camshaft holder points towards the cam
chain. Tighten the bolts evenly and a little at a
time in a criss-cross pattern, working from the
centre of the camshaft outwards, to the torque
setting specified at the beginning of the Chapter
(see illustration 8.26b).
Whilst tightening the
bolts, make sure the holders are being pulled
squarely down and are not binding on the
dowels. While doing this, don't let the camshafts
rotate.
16
Now unscrew the bolts a evenly and a little
at a time in a criss-cross pattern, and carefully lift
off the camshaft holders.
17
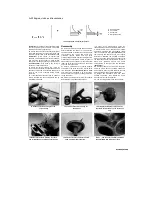
To determine the oil clearance, compare the
crushed Plastigauge (at its widest point) on each
journal to the scale printed on the Plastigauge
container
(see illustration).
Compare the results
to this Chapter's Specifications. If the oil
clearance is greater than specified, measure the
diameter of the cam bearing journal with a
micrometer
(see illustration).
If the journal
diameter is less than the specified limit, renew
the camshaft and recheck the clearance. If the
clearance is still too great, renew the cylinder
head and holders.
[flflfl|g!|
Before renewing camshafts
or the holders because of
damage, check with local
machine shops specialising in
motorcycle engine work. In the case of the
camshafts, it may be possible for cam lobes
to be welded, reground and hardened, at a
cost far lower than that of a new camshaft.
If the bearing surfaces in the holders are
damaged, it may be possible for them to be
bored out to accept bearing inserts. Due to
the cost of new components it is
recommended that all options be explored
before condemning them as trash!
18
Except in cases of oil starvation, the cam
chain wears very little. If the chain has stretched
excessively, which makes it difficult to maintain
proper tension, or if it is stiff or the links are
binding or kinking, renew it. Refer to Section 24
for the procedure.
19 Check the sprockets for wear, cracks and
other damage. If the sprockets are worn, the cam
chain is also worn, and so is the sprocket on the
crankshaft. If severe wear is apparent, the entire
engine should be disassembled for inspection.
8.17a Compare the width of the crushed Plastigauge to the scale
printed on the Plastigauge container
8.17b Measure the cam bearing journals with a micrometer
Staned by Stalker
SB
HINT
HiAIT