- 130 -
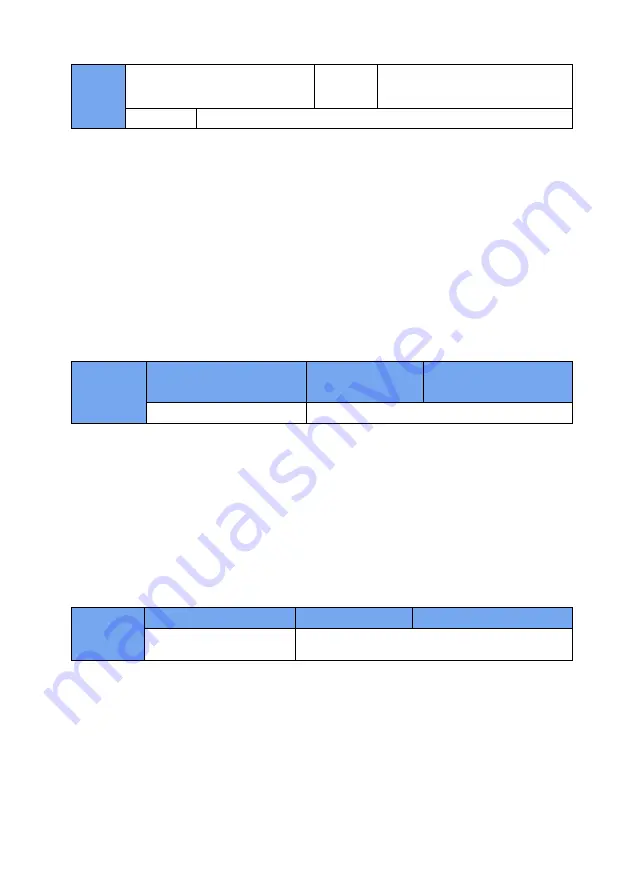
A0-08
Torque control deceleration time
Factory
default
0.00s
Set range
0.00s
~
65000s
In the torque control mode, the difference between the output torque and the load torque
of the motor determines the speed change rate of the motor and the load. Therefore, the
motor speed may change rapidly, resulting in excessive noise or mechanical stress. By
setting the torque control acceleration / deceleration time, the motor speed can be changed
gently.
However, if the torque response is required, it is necessary to set the torque control
acceleration / deceleration time to 0.00s.
For example: two motor hard link drag the same load, in order to ensure uniform
distribution of the load, set a frequency converter for the host, the use of speed control,
another inverter for the machine and the use of torque control, the actual output of the host
Moment as the torque command from the slave, then the torque of the slave machine needs
to follow the host quickly, then the torque control acceleration / deceleration time of the
slave is 0.00s.
A5 Group Control optimization parameters
A5-00
DPWM Switch the upper
limit frequency
Factory default
8.00Hz
Set range
5.00Hz
~
max frequency
Only valid for VF control.
Asynchronous machine VF running time to determine the way, below this value for the 7-
segment continuous modulation mode, on the contrary for the 5-segment intermittent
modulation.
The switching loss of the inverter is larger when the 7-stage continuous modulation is larger,
but the current ripple is smaller. The switching loss is smaller and the current ripple is larger
in the 5-stage intermittent modulation mode, but it may lead to high frequency The instability
of the motor operation, generally do not need to be modified.
Refer to function code P3-11 for VF operation instability. Refer to function code P0-15 for
inverter loss and temperature rise.
A5-01
PWM Modulation mode
Factory default
0
Set range
0: Asynchronous modulation 1: Synchronous
modulation
Only valid for VF control.
Synchronous modulation, refers to the carrier frequency with the output frequency
conversion and linear changes to ensure that the ratio of the two (carrier ratio) unchanged,
generally used in the output frequency is high, is conducive to the output voltage quality.
At lower output frequencies (below 100 Hz), it is generally not necessary to synchronize the
modulation because the ratio of the carrier frequency to the output frequency is relatively
high and the asynchronous modulation advantage is more pronounced.
When the operating frequency is higher than 85Hz, the synchronous modulation takes effect,
and the frequency is fixed as asynchronous modulation mode.
















































