13
that within 2 years through a power, power time of at least 5 hours, the input voltage
must be slowly raised to the rated voltage regulator.
2.7 Guide for Selection of Brake Components
(*): Figure 2-1 is the guide data, the user can choose according to the actual situation of
different resistance and power, (but the resistance must not be less than the
recommended value in the table, the power can be large.) The choice of braking resistor
The actual application of the motor power generation to determine the power, and system
inertia, deceleration time, bit energy load and so have a relationship, the need for
customers according to the actual situation. The greater the inertia of the system, the
shorter the deceleration time required, the more frequent the braking, the greater the
choice of the braking resistor, the smaller the resistance.
2.7.1 The choice of resistance
When braking, the regenerative energy of the motor is almost entirely consumed on the
braking resistor. According to the formula: U * U / R = Pb
Formula U - System Brake Voltage for Stable Braking
(Different systems are not the same, for the 380VAC system generally take 700V)
Pb ---- brake power
2.7.2 Power selection of braking resistor
The braking power is theoretically the same as the brake power, but the derating is 70%.
According to the formula: 0.7 * Pr = Pb * D
Pr - the power of the resistor
D ---- Brake frequency (regeneration process the proportion of the entire process)
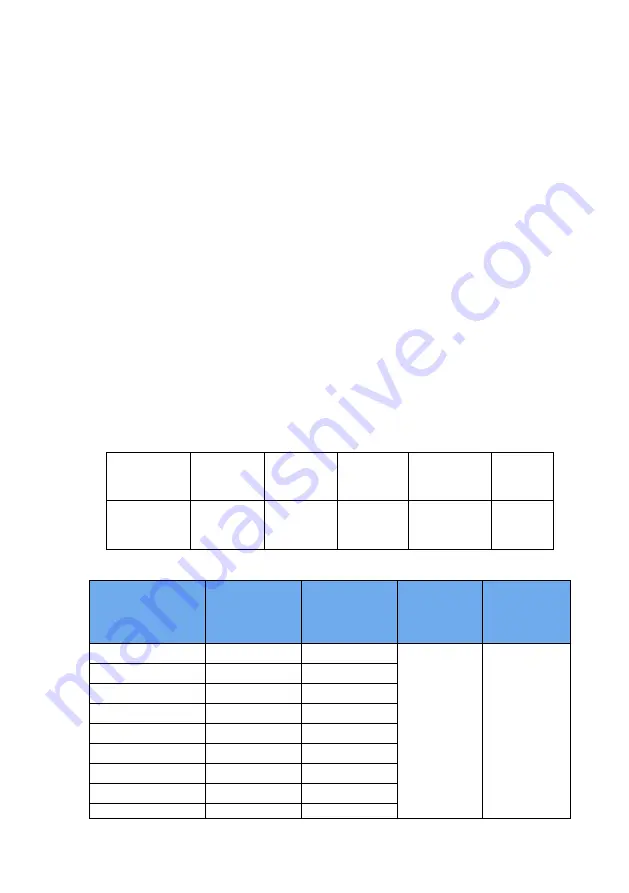
Normal
case
Elevator
Open and
take
Centrifug
e
accidental
braking
resistor
Normal
use
Brake
frequency
value
20%
~30%
-20 ~30%
50%~60
%
-5%
10%
Model Type
Braking
resistor
Recommended
power
Recommended
resistance
Recommended
resistance
brake unit
Notes
DSI-200-K40G1
80W
≥
200Ω
Standard
built-in
No special
instructions
DSI-200-K75G1
80W
≥
150Ω
DSI-200-1K5G1
100W
≥
100Ω
DSI-200-2K2G1
100W
≥
70Ω
DSI-200-K75G3
150W
≥
300Ω
DSI-200-1K5G3
150W
≥
220Ω
DSI-200-2K2G3
250W
≥
200Ω
DSI-200004G3/5K5P3
300W
≥
130Ω
DSI-2005K5G3/7K5P3
400W
≥
90Ω














































