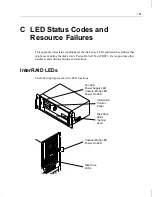
149
10 Configuring the Disk Array for
Performance
This chapter discusses RAID performance and configuration methods of the hard disk
drives. Included are examples for striped, mirrored, and other performance options and a
brief discussion of database applications. Also included are the differences in RAID mode
performance and data integrity.
RAID Technology
Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks (RAID) increases system performance and gives an
extra level of data protection. The basic idea of RAID technology is to use multiple hard
disk drives as a single logical drive. Several hard disk drives are arranged into a pack and
then defined as a logical system drive. Data may then be striped or mirrored across the
physical drives. Striping spreads data across three or more drives, which allows more disk
drive heads to access data, and thereby improves data throughput. Mirroring places a copy
of the data on two mirrored drives to offer data protection in the event a hard disk drive
should fail.
Striped RAID Performance
You can achieve performance improvement on a multi-channel RAID controller for striped
data (such as RAID 0 or RAID 5) when the drives in the packs span the input/output (I/O)
channels. For example, perform the following when creating a pack containing four hard
disk drives:
u
Place the first disk drive in the pack on the first I/O channel of the RAID controller.
u
Place the second disk drive in the pack on the second I/O channel of the RAID
controller.
u
Place the third disk drive in the pack on the first I/O channel of the RAID controller.
u
Place the fourth disk drive in the pack on the second I/O channel of the RAID
controller.
Summary of Contents for InterRAID-12
Page 1: ...InterRAID Hardware User s Guide January 1997 DHA018210 ...
Page 4: ......
Page 121: ...106 ...
Page 157: ...142 ...
Page 163: ...148 ...
Page 171: ...156 ...