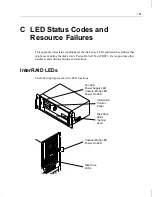
152
For maximum performance in a database, Log or Redo Log access is sequential I/O data; you
should separate sequential I/O data from random I/O data.
Data access is usually random for On-line Transaction Processing (OLTP) applications. The
optimal performance strategy is to stripe the data across devices to distribute the I/O data and
minimize I/O contention. OLTP applications perform operations on small blocks of data
randomly spread across multiple data pages.
Decision Support Systems (DSS) and Data Warehouse applications may benefit from large
block I/O if they are performing large sequential reads of adjacent data pages. Refer to the
documentation for your database system to determine if you can modify the I/O block size.
RAID Mode Performance and Data Integrity
Differences
Three RAID modes provide improved data integrity through data redundancy: RAID 1,
RAID 5, and RAID 3. RAID 0 does not provide data redundancy.
RAID 1 (mirroring) has the smallest impact on performance. It provides neither a severe
performance penalty nor a boost. However, mirroring requires 50% of the raw disk space in
the pack for data redundancy.
RAID 5 (striped data with parity) has improved performance on reads. Write performance is
less due to the time required to calculate parity by performing read-modify-writes on small
block transfers. RAID 5 is more efficient than RAID 1 in terms of the disk space used for
redundancy. A RAID 5 stripe with N disks uses N-1 disks for data, and only one disk for
parity and redundancy information.
RAID 3 is similar to RAID 5, except it stores all parity information on a single disk in the
pack rather than distribute it among the disks as in RAID 5. RAID 3 performance and
space-efficiency characteristics are similar to RAID 5, but RAID 3 provides better
performance for large-block, sequential transfers when using the Controller Read Ahead
option.
RAID 0 (striped data without parity) provides no data redundancy, and thus, no assurance of
data integrity. Data distributes across multiple disk drives; consequently, a failure in any of
the disk drives could result in loss of that data. RAID 0 provides less data integrity than a
single disk drive. However, the performance improvements available through the use of
RAID 0 are greatest. It allows concurrent access to multiple disks on both reads and writes
without the write performance penalty associated with RAID 5.
Summary of Contents for InterRAID-12
Page 1: ...InterRAID Hardware User s Guide January 1997 DHA018210 ...
Page 4: ......
Page 121: ...106 ...
Page 157: ...142 ...
Page 163: ...148 ...
Page 171: ...156 ...