Goto
This function allows you to move directly to a point on the graph without
having to trace along the graph. It is very powerful and useful.
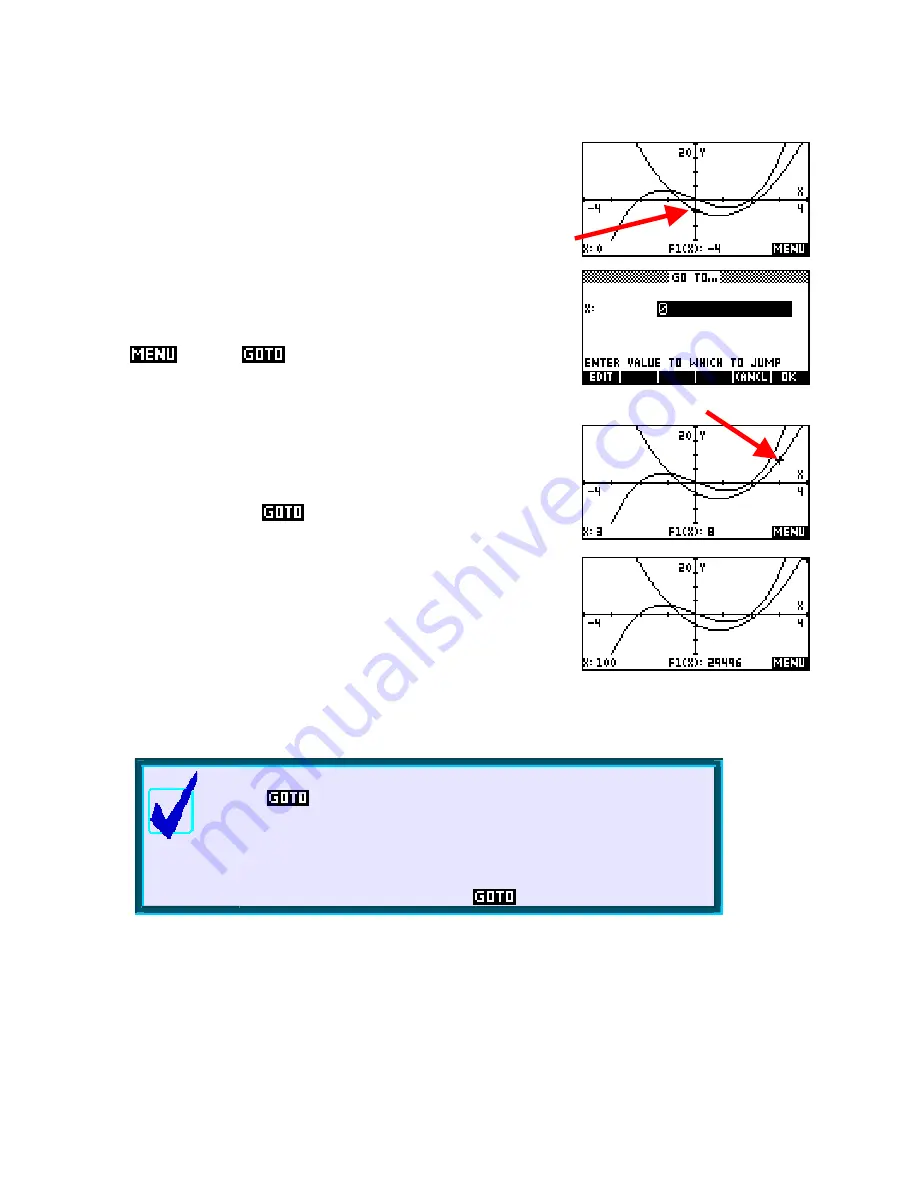
Suppose we begin with the cursor at x = 0 on
F1(X)
as shown right.
and then
to see the input form shown right.
Press
Type the value 3 and press
ENTER
. The cursor will jump straight to the
value x = 3, displaying the (X,Y) coordinates at the bottom of the screen.
A very nice feature of the
key is that it will jump to values
which are not on the current screen, or which would be inaccessible for
the current scale.
For example, we can jump to the value x = 100 and see the (X,Y)
coordinate displayed, with the cursor positioned at the far right side of
the screen. Similarly, you could jump to the value x =
√
2 despite this
value being inaccessible for the scale chosen, since the cursor will
normally only move to the values defined by the dots on the screen.
Calculator Tip
The
lated values.
2
+2.
Isect
to that point.
See
page 58 for information on
Isect
.
.
key will also accept calcu
You could, for
example, jump to a value such as e
If you had recently found an
intersection, then jumping to a value of
would return the cursor
This is useful when finding areas between functions.
See page 70 for an example of
finding areas between curves using
54






























