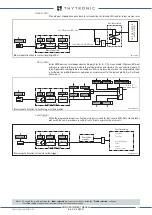
58
FUNCTION CHARACTERISTICS
Sequence
• Fundamental RMS positive sequence current:
I
1
• Fundamental RMS negative sequence current:
I
2
• Fundamental RMS positive sequence voltage:
U
1
• Fundamental RMS negative sequence voltage:
U
2
Demand
• Fixed demand (
I
L1FIX
,
I
L2FIX
,
I
L3FIX
, ±
P
FIX
, ±
Q
FIX
)
Inside an adjustable time interval
t
FIX
, an average magnitude is calculated for phase currents
I
L1
,
I
L2
,
I
L3
, active power ±
P
and reactive power ±
Q
of measures taken every second. The average va-
lues are stored at the end of the same time interval.
• Rolling demand (
I
L1ROL
,
I
L2ROL
,
I
L3ROL
, ±
P
ROL
, ±
Q
ROL
)
Inside an adjustable time interval
N
ROL
∙
t
ROL
, an average magnitude is calculated for phase curren-
ts
I
L1
,
I
L2
,
I
L3
, active power ±
P
and reactive power ±
Q
of measures taken every second, where
t
ROL
is
the length of any time subinterval and
N
ROL
is the number of the time intervals. The average values
are stored at the end of the same time subinterval.
• Peak (
I
L1MAX
,
I
L2MAX
,
I
L3MAX
, ±
P
MAX
, ±
Q
MAX
)
Inside an adjustable time interval
t
ROL
, the maximum magnitude is calculated for phase currents
I
L1
,
I
L2
,
I
L3
, active power ±
P
and reactive power ±
Q
of measures taken every second. The average
values are stored at the end of the same time interval
t
ROL
(Rolling demand common parameter).
I1-I2.ai
I
L1
I
1
, I
2
I
2
= (
I
L1
+ e
-j120°
I
L 2
+ e
+j120°
I
L 3
) / 3
I
1
= (
I
L1
+ e
+j120°
I
L 2
+ e
-j120°
I
L 3
) / 3
I
L3
I
L2
(
I
n
)
e
-j120°
= -
√3
j
1
2
2
-
e
+j120°
= -
√3
j
1
2
2
+
U2.ai
U
L1
U
1
, U
2
U
2
= (
U
L1
+ e
-j120°
U
L 2
+ e
+j120°
U
L 3
) / 3
U
1
= (
U
L1
+ e
+j120°
U
L 2
+ e
-j120°
U
L 3
) / 3
U
L3
U
L2
e
-j120°
= -
√3
j
1
2
2
-
e
+j120°
= -
√3
j
1
2
2
+
(
u
n
)
Fix-Demand.ai
1s
I
L1FIX
,
I
L 2FIX
,
I
L 3FIX
±
P
FIX
t
FIX
±
P
±
Q
(
I
n
)
(
P
n
)
(
Q
n
)
±
Q
FIX
I
L2
I
L1
I
L3
I
L xFIX
I
L xn
t
FIX
∙ 60
t
FIX
∙ 60
n=1
∑
1
±
Q
FIX
=
±
Q
n
t
FIX
∙ 60
t
FIX
∙ 60
n=1
∑
1
±
P
FIX
=
±
P
n
t
FIX
∙ 60
t
FIX
∙ 60
n=1
∑
1
t
FIX
t
FIX
t
FIX
Rol-Demand.ai
Rolling demand example with
N
ROL=4
I
L1ROL
I
L 2ROL
I
L 3ROL
±
P
ROL
±
P
±
Q
(
I
n
)
(
P
n
)
(
Q
n
)
±
Q
ROL
I
L2
I
L1
I
L3
0
1
2
3
4
5
1s
t
ROL
t
ROL
N
ROL
t
ROL
t
ROL
t
ROL
6
t
ROL
Average inside subinterval
t
ROL
I
L xROL
=
I
L xk
t
ROL
∙60
t
R OL
∙60
k=1
∑
N
R OL
n=1
n
∑
1
N
ROL
1
±
P
ROL
=
±
P
k
t
ROL
∙60
t
R OL
∙60
k=1
∑
N
R OL
n=1
n
∑
1
N
ROL
1
±
Q
ROL
=
±
Q
k
t
ROL
∙60
t
R OL
∙60
k=1
∑
N
R OL
n=1
n
∑
1
N
ROL
1
Max-Demand.ai
Maximum value of averages inside time interval
t
ROL
Average inside time interval
t
ROL
I
L1MA X
I
L 2MA X
I
L 3MA X
±
P
MA X
±
P
±
Q
(
I
n
)
(
P
n
)
(
Q
n
)
±
Q
MA X
I
L2
I
L1
I
L3
1s
t
ROL
t
ROL
t
ROL
t
ROL
t
ROL
t
ROL
MAX
I
L xMA X
=
I
L xn
t
ROL
∙60
t
R OL
∙60
n=1
∑
1
MAX
±
P
MA X
=
±
P
n
t
ROL
∙60
t
R OL
∙60
n=1
∑
1
MAX
±
Q
MA X
=
±
Q
n
t
ROL
∙60
t
R OL
∙60
n=1
∑
1
XMR-D EQUIPMENT MANUAL
Ed. 2.9 - 02/2021