Medium Optical Disk (RW551/RW552) Library
6–2
EK–MOL80–SV. B01
Autochanger Robotics
Movements
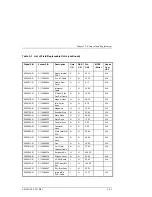
The mechanism code of the autochanger accepts high-level SCSI commands
from the interface, translates these commands into servo code for the
autochanger, executes the command, and reports status.
When a SCSI command is received, it is translated into a series of smaller
submoves in the servo code of the autochanger and executed.
Figure 6–1 SCSI Command Translation For Autochanger Operation
Examples of high-level SCSI-2 commands are:
•
Move/Exchange – move a cartridge from element A to element B
•
Seek – position the transport at a target element
•
Test – test for the presence of a cartridge at a target element
•
Actuate mailslot – rotate the mailslot assembly to perform I/O with the user
The commands are translated into a series of moves which are basic autochanger
functions. These submoves are called macro-moves. In this jukebox the macro-
moves are as follows.
•
move carriage – position the picker transport to a specific vertical position
•
flip – rotate the picker
•
cartridge I/O – plunge and retrieve the picker finger assembly to move
cartridges between the picker and magazines, drives, or the mailslot.
•
rotate mailslot – plunge and retrieve the picker finger assembly to rotate the
mailslot assembly toward and away from the user.