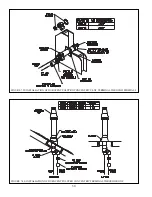
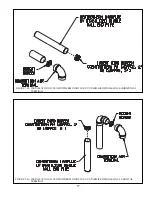
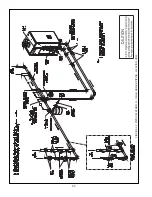
64
IX System Piping
A. General System Piping Precautions
"&
0
(BBBB*)()BBB)*
((-
0
*))BB)?IBB@
B@@-J(*BAI(B)@-J-
0
$+)*??(*
)B*(-AB*)(*
+)*?I)J*((B(*D(
?-
WATER QUALITY AND BOILER WATER ADDITIVES
IMPORTANT NOTE
The heat exchanger used in this boiler is made from stainless steel coils having relatively narrow waterways. Once
&' #'\ ' [&# \' %& &&
from the system. Take the following precautions to minimize the chance of severe heat exchanger damage caused by
corrosion and/or overheating:
^## %# \# %#' )
\#& \&*\#) %\&& && )) #
'\& # '' *&) ## &
above. Flush the system completely and repeat if necessary to completely remove these contaminants. If necessary,
a cleaning agent may be used to assist in system cleaning. See Part XI (“Start-up and Check-out”) for recommended
cleaners.
2. Make sure that the system is tight - This is the single most important guideline. Tap water contains dissolved
oxygen which causes corrosion. In a tight system, this oxygen comes out of solution and is quickly removed from
the system through the automatic air vent. The system then remains essentially free of oxygen. If the system is not
tight, however, frequent additions of make-up water can expose the heat exchanger to oxygen on a continuous basis.
In addition, frequent additions of hard make-up water can cause calcium deposits to collect in the heat exchanger,
causing severe damage. To minimize additions of make-up water:
Q
##%# % )
Q
# &&%& %\# % '# # %#%&&\ &
isolating the boiler from the system with a heat exchanger.
Q
##* {&& %&& \# ))
open frequently, resulting in regular additions of make-up water.
Q
)) &\ ' # %&&
so that routine additions of make-up water can be detected and their cause corrected.
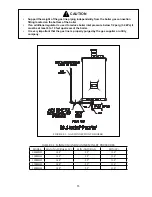
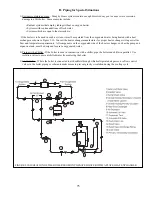
3. Non-Metallic Tubing - Even if the system is tight, oxygen can be introduced into the system through some
types of non-metallic tubing used in radiant or snow melt systems. Other nonmetallic tubing is equipped with an
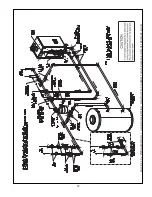
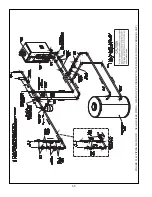
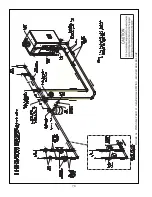
oxygen barrier to prevent migration of oxygen into the water. If the boiler is to be installed in a system containing
non-metallic tubing without an oxygen barrier, it must be isolated from the boiler with a heat exchanger as shown in
Figure 9.10.
4. Water Chemistry, Antifreeze, and Boiler Water Additives – Improper boiler water chemistry can cause the heat
exchanger damage described above, as well as deterioration of seals. Observe the water chemistry requirements
shown in Part XI (“Start-up and Check-out”).
Summary of Contents for PHNTM080
Page 2: ......
Page 9: ...7 Figure 4 1 Minimum Clearances To Combustible Construction...
Page 11: ...9 Figure 5 1 Wall Layout Mounting Hole Location...
Page 12: ...10 Figure 5 2 Boiler Mounting Bracket Installation Boiler Wall Mounting...
Page 39: ...37 FIGURE 7 24 SPLIT VENT SYSTEM FLEX IN ABANDONED MASONRY CHIMNEY VENT OPTIONS 33 38...
Page 63: ...61 This page is intentionally left blank...
Page 68: ...66 FIGURE 9 2 PIPING METHOD 1 NEAR BOILER PIPING HEATING ONLY...
Page 72: ...70 FIGURE 9 6 PIPING METHOD 1 NEAR BOILER PIPING SHADED BOILER LOOP...
Page 82: ...80 FIGURE 10 4 PROPER INSTALLATION OF HEADER SENSOR...
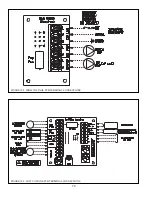
Page 84: ...82 FIGURE 10 6 INTERNAL WIRING CONNECTIONS DIAGRAM...
Page 85: ...83...
Page 92: ...90 Lighting and Operating Instructions...
Page 101: ...99 FIGURE 12 5 SETTINGS MENU SEE PART C FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION...
Page 113: ...111 FIGURE 13 2 IGNITION ELECTRODE GAP FIGURE 13 3 CONDENSATE TRAP EXPLODED PARTS VIEW...
Page 125: ...123...
Page 127: ...125 40 33 31 27 28 34 35 37 38 32 39 36 29 30 48 Blower Gas Valve Assembly for 80 100 120...
Page 129: ...127...
Page 131: ...129...
Page 132: ...130...
Page 133: ...131...
Page 135: ...133...
Page 137: ...135 140 141 142 143 144 145...