778
TORQUE CONTROL
In this function, a limit is established for the resistance torque applied to the motor used for positioning. The
power is turned OFF if torque exceeding that value is applied to the motor.
When excessive torque is applied to a motor, it causes the current to suddenly increase. Motor burning and other
stress on the motor occurs, and the life of the motor is shortened.
This function utilizes the sudden increase in the torque when the machine OPR to issue a command to stop the
motor.
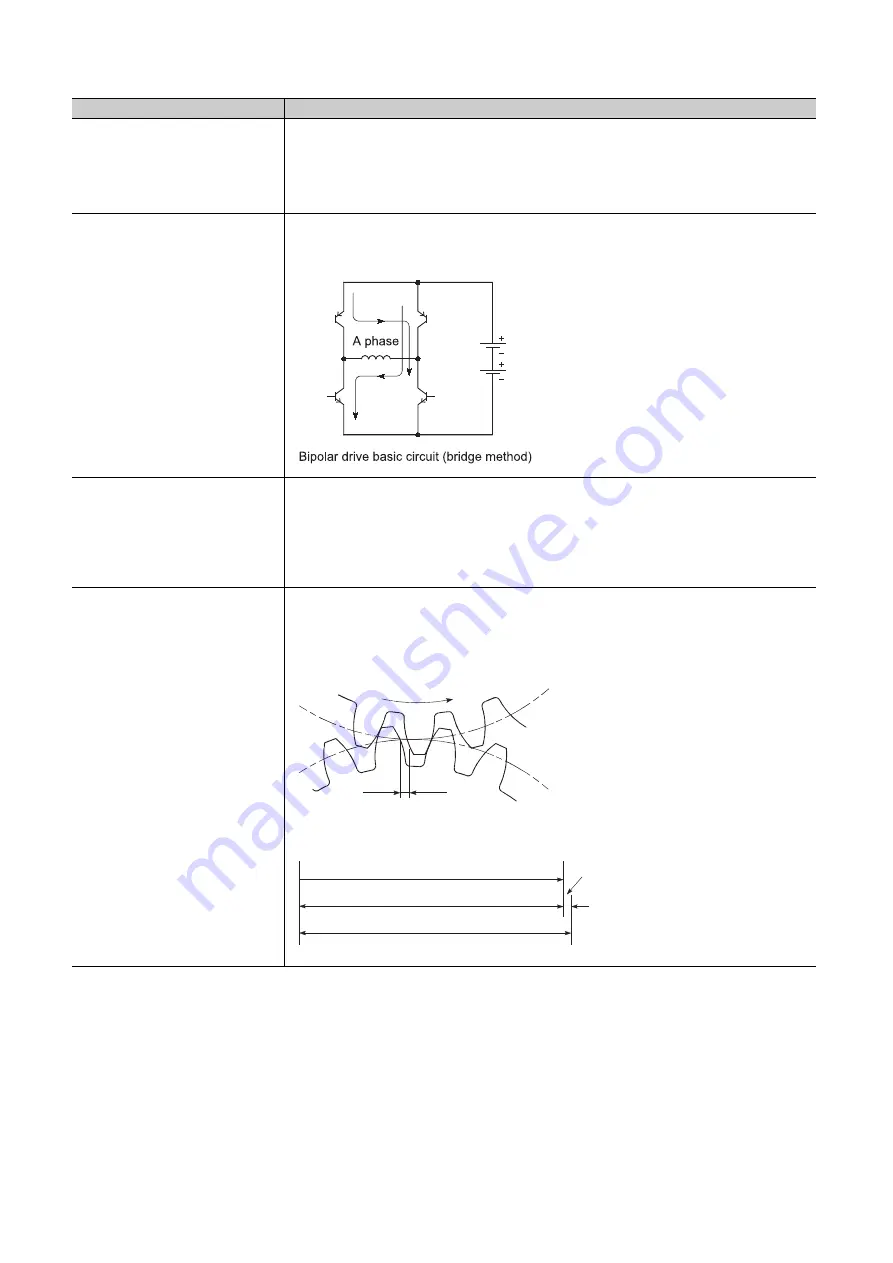
BIPOLAR DRIVE CONSTANT-CURRENT
SYSTEM
This is one system for driving a stepping motor. In this method, the orientation of the excitation current flowing to
the stator coil is reversed, and the excitation current direction is in both the positive and negative direction. This
enables the motor coil to be used effectively, and a large output torque can be obtained at low speeds.
BACKUP FUNCTION
• Functions for storing the program and device statuses stored in the RAM memory of the CPU module, so that
they are not lost during power failures, etc.
• Functions for storing the current value in absolute position compatible systems so that it is not lost during
power failures, etc.
• Functions for reading the CPU module data (programs, parameters, positioning data, etc.) by GX Works2
when the old CPU module is replaced, and then write it to the new CPU module after the replacement is
completed.
BACKLASH COMPENSATION
When a forward run operation changes to a reverse run operation, there is sometimes play (backlash) in the
mesh of the toothed gears. This also occurs when using a worm gear. Because of this backlash, a left feed of 1m
(3.28feet) carried out after a right feed of 1m (3.28feet) will not be sufficient to return the machine to its original
position. The machine cannot be positioned to its original position without an extra feed equivalent to the
backlash amount. This function compensates for that backlash amount.
Term
Description
Backlash
Forward run
1m (3.28feet) (right feed)
Machine
does not
move.
Backlash
1m (3.28feet) (left feed)
(Left feed amount)
Содержание MELSEC-L LD75D
Страница 1: ...MELSEC L LD75P LD75D Positioning Module User s Manual LD75P1 LD75P2 LD75P4 LD75D1 LD75D2 LD75D4 ...
Страница 2: ......
Страница 11: ...9 Memo ...
Страница 47: ...45 CHAPTER 2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION 2 2 1 General Image of System 1 When connected to a CPU module ...
Страница 176: ...174 ...
Страница 264: ...262 ...
Страница 266: ...264 ...
Страница 267: ...265 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Страница 268: ...266 ...
Страница 269: ...267 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Страница 270: ...268 ...
Страница 271: ...269 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Страница 272: ...270 Z ABRST1 instruction execution ...
Страница 273: ...271 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Страница 278: ...276 ...
Страница 279: ...277 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Страница 280: ...278 ...
Страница 281: ...279 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Страница 282: ...280 ...
Страница 283: ...281 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Страница 284: ...282 ...
Страница 285: ...283 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Страница 286: ...284 ...
Страница 287: ...285 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Страница 316: ...314 Memo ...
Страница 685: ...683 APPENDICES A Appendix 1 Function Update Appendix 1 1 Function comparison Memo ...
Страница 738: ...736 Memo ...
Страница 806: ...804 5 LD75D2 Unit mm 6 LD75D4 Unit mm 45 4 90 4 95 4 45 45 DIN rail center 45 4 90 4 95 4 45 45 DIN rail center ...
Страница 817: ......
















































