773
APPENDICES
A
Appendix
8
ME
LSE
C
E
xplanat
ion
of
Pos
itioning T
e
rm
s
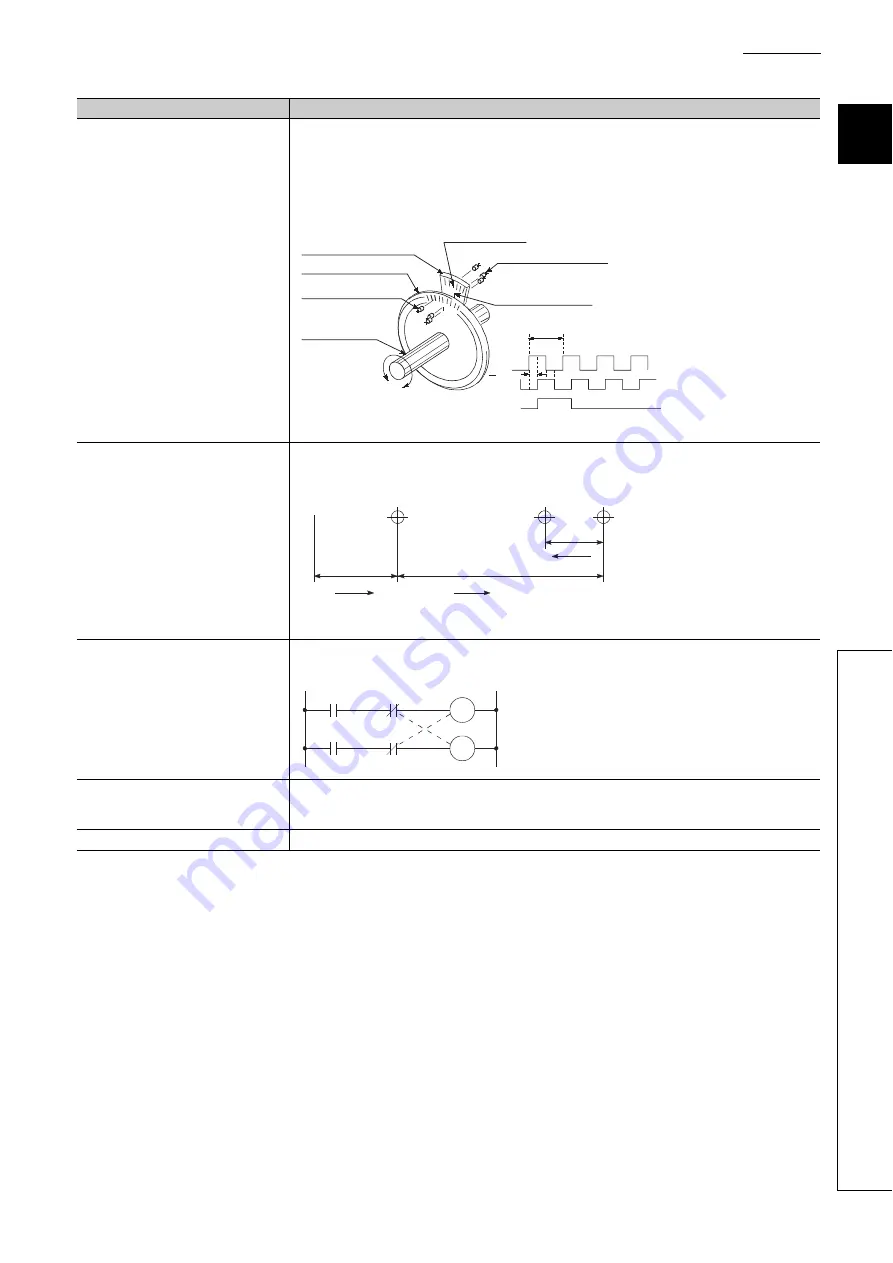
INCREMENTAL ENCODER
A device that simply outputs ON/OFF pulses by the rotation of the axis. 1-phase types output only A pulses, and
do not indicate the axis rotation direction. 2-phase types output both A and B pulse trains, and can judge the
rotation direction. The direction is judged to be forward if the B pulse train turns ON when A is ON, and judged to
be reverse if A turns ON when B is ON. There is also another type of incremental encoder with a zero signal. The
most commonly used incremental encoders output between 100 and 10,000 pulses per axis rotation. Refer to the
term "ENCODER".
INCREMENTAL SYSTEM
The current value is 0 in this system. Positions are expressed by the designated direction and distance of travel.
Also called the relative address system. This system is used in fixed-feed, etc. Compare ABSOLUTE SYSTEM.
INTERLOCK
In this condition, the machine is blocked from moving to the next operation until the operation in progress is
complete. This function is used to prevent damage to devices and malfunctioning.
INVERTER
This refers to a device to change a direct current (DC) to an alternating current (AC). The device actually
changes the motor speed by changing 50Hz or 60Hz of commercial frequency to direct current once, then
changing it again to a 5 to 120Hz alternating current and controlling the motor speed.
ERROR RESET
This resets error of axis. Note that if the cause of the error is not eliminated at that time, the error will occur again.
Term
Description
A
B
A
B
Z
1
4
A signal slit
B signal slit
Lighting emitting diode
Zero signal slit
2-phase + OP output
1 pulse per axis rotation
Output waveform
Zero signal
Rotating axis
Phototransistor
Slit disk
1 pitch
pitch
3
.
o
N
2
.
o
N
1
.
o
N
0
0
0
Stop
Left
Right
Right No. 2 is several millimeters
to the right of No. 1.
Y1
Y0
Y0
Y1
Forward run
Reverse run
Содержание MELSEC-L LD75D
Страница 1: ...MELSEC L LD75P LD75D Positioning Module User s Manual LD75P1 LD75P2 LD75P4 LD75D1 LD75D2 LD75D4 ...
Страница 2: ......
Страница 11: ...9 Memo ...
Страница 47: ...45 CHAPTER 2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION 2 2 1 General Image of System 1 When connected to a CPU module ...
Страница 176: ...174 ...
Страница 264: ...262 ...
Страница 266: ...264 ...
Страница 267: ...265 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Страница 268: ...266 ...
Страница 269: ...267 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Страница 270: ...268 ...
Страница 271: ...269 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Страница 272: ...270 Z ABRST1 instruction execution ...
Страница 273: ...271 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Страница 278: ...276 ...
Страница 279: ...277 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Страница 280: ...278 ...
Страница 281: ...279 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Страница 282: ...280 ...
Страница 283: ...281 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Страница 284: ...282 ...
Страница 285: ...283 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Страница 286: ...284 ...
Страница 287: ...285 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Страница 316: ...314 Memo ...
Страница 685: ...683 APPENDICES A Appendix 1 Function Update Appendix 1 1 Function comparison Memo ...
Страница 738: ...736 Memo ...
Страница 806: ...804 5 LD75D2 Unit mm 6 LD75D4 Unit mm 45 4 90 4 95 4 45 45 DIN rail center 45 4 90 4 95 4 45 45 DIN rail center ...
Страница 817: ......
















































