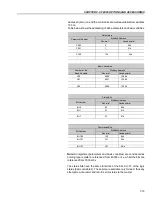
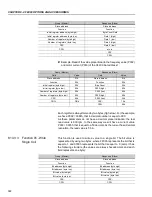
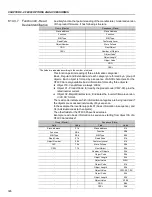
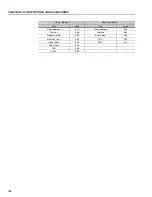
Reviews:
No comments
Related manuals for CFW-09

AF-650 GP Series
Brand: GE Pages: 212

AF-60 LP
Brand: GE Pages: 86

Kinetix 2071-A10
Brand: Allen-Bradley Pages: 20

DQ-100-4
Brand: EKSMA OPTICS Pages: 12

ND-3530
Brand: NEC Pages: 18

ND-3550A
Brand: NEC Pages: 18

ND-3540A
Brand: NEC Pages: 18

ND-3520A
Brand: NEC Pages: 18

VERSA LXI VERSABAY III DVD-ROM DRIVE
Brand: NEC Pages: 8

10.300
Brand: BTR Pages: 28

EM S Tandem AC
Brand: STG-BEIKIRCH Pages: 25

SDP Series
Brand: Shihlin electric Pages: 555

JOLLY BIG ONE
Brand: RIB Pages: 44

Mini
Brand: Iomega Pages: 32

P20B10150D
Brand: Sanyo Denki Pages: 119

PS6 Series
Brand: Stober Pages: 264

iPOS4803-SY
Brand: Technosoft Pages: 36

iPOS4808 MYCAN-STO
Brand: Technosoft Pages: 45