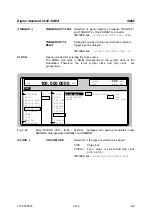
Digital Standard W-CDMA (NTT DoCoMo/ARIB 0.0)
SMIQ
1125.5555.03
E-9
2.152
2.13.1
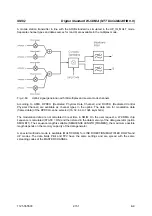
Sync and Trigger Signals
A chip sequence is calculated for the generation of W-CDMA signals and stored in the memory of the
data generator (option SMIQB11). This chip sequence can be run repetitively (TRIGGER MODE
AUTO).
Trigger signals can be used for synchronized measurements on receivers (TRIGGER MODE RETRIG,
ARMED_AUTO or ARMED_RETRIG).
A trigger signal can be fed via the TRIGIN input at connector PAR DATA of SMIQ. The chip sequence
either starts immediately after the active slope of the trigger signal or after a settable number of chips
(EXT TRIGGER DELAY). Retriggering (RETRIG) can be inhibited for a settable number of chips (EXT
RETRIGGER INHIBIT).
A trigger event can be executed manually or via the IEC/IEEE bus using EXECUTE TRIGGER.
When a trigger event is executed, a trigger signal is output at the TRIGOUT 3 output of SMIQ.
SMIQ generates the following sync signals:
•
a 0.625 ms slot clock
•
a 10 ms radio frame clock
•
a marker signal for identifying the periodic repetition of the generated chip sequence
SMIQ can output two of the three signals via pins TRIGOUT 1 and 2 of connector PAR DATA.
A clock synthesizer on the modulation coder generates the chip clock in the SMIQ. All the clock signals
are synchronized to the 10-MHz reference of the SMIQ. The chip clock is available at connector
SYMBOL CLOCK. If required, the clock synthesizer in the SMIQ can be synchronized to an external
chip clock which is fed in at connector SYMBOL CLOCK.
To allow for a trouble-free synchronization of the clock synthesizer first apply the external clock and set
the correct chip rate at SMIQ (MODULATION - CHIPRATE VARIATION). Then switch CLOCK
SOURCE from INT to EXT.
Note:
The set symbol rate should not differ by more than 1% from the symbol rate of the external
signal.