CHAPTER 15 STANDBY FUNCTION
Preliminary User’s Manual U16846EJ1V0UD
299
(b) Release by RESET input
When the RESET signal is input, HALT mode is released, and then, as in the case with a normal reset
operation, the program is executed after branching to the reset vector address.
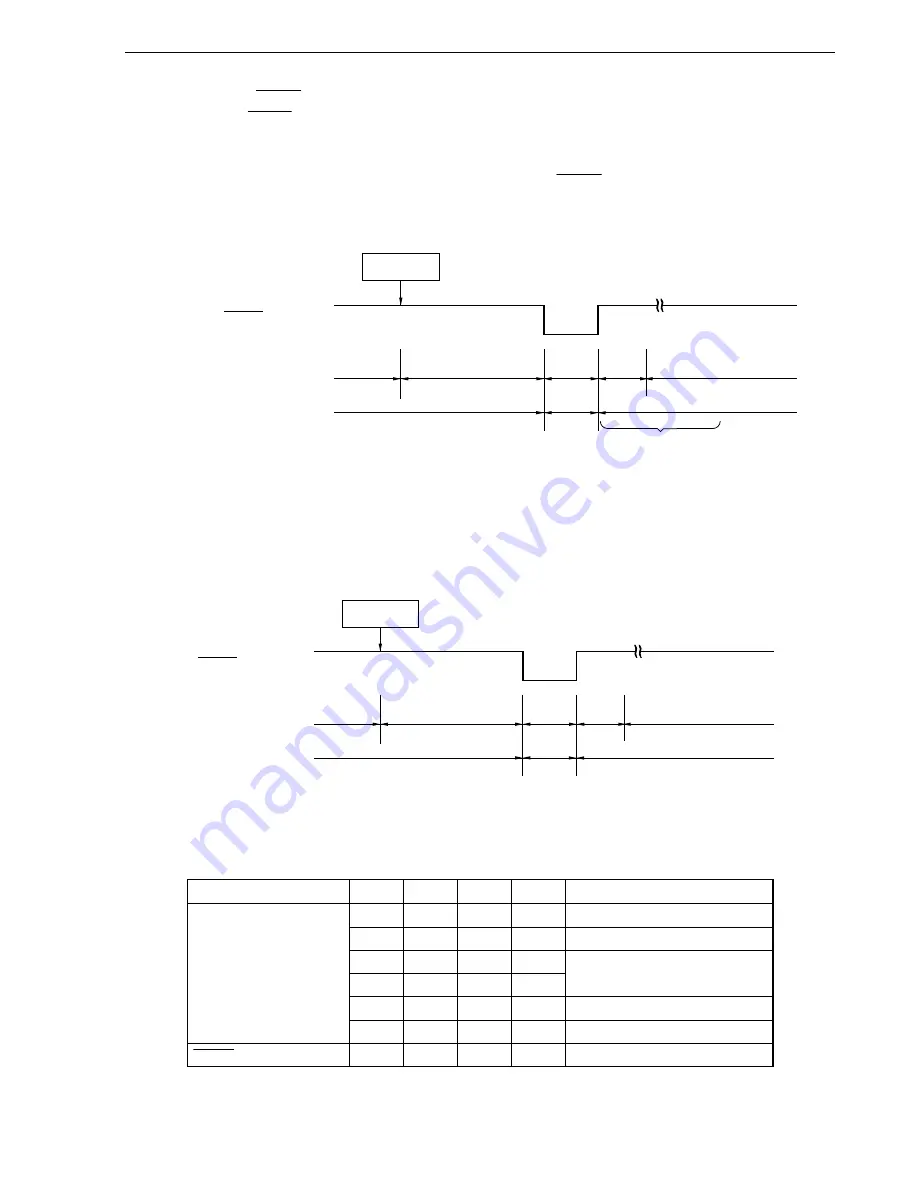
Figure 15-4. HALT Mode Release by RESET Input
(1) When high-speed system clock is used as CPU clock
HALT
instruction
RESET signal
High-speed system clock
Operating mode
HALT mode
Reset
period
Operation
stopped
Operating mode
Oscillates
Oscillation
stopped
Oscillates
Status of CPU
(High-speed
system clock)
Oscillation stabilization time
(2
11
/f
XP
to 2
16
/f
XP
)
Note
(Ring-OSC clock)
(17/f
R
)
Note Waiting for the oscillation stabilization time is not required when the external RC oscillation clock is
selected as the high-speed system clock by the option byte. Therefore, the CPU clock can be
switched without reading the OSTC value.
(2) When Ring-OSC clock is used as CPU clock
HALT
instruction
RESET signal
Ring-OSC clock
Operating mode
HALT mode
Reset
period
Operation
stopped
Operating mode
Oscillates
Oscillation
stopped
Oscillates
Status of CPU
(Ring-OSC clock)
(17/f
R
)
(Ring-OSC clock)
Remarks 1. f
XP
: High-speed system clock oscillation frequency
2. f
R
: Ring-OSC clock oscillation frequency
Table 15-3. Operation in Response to Interrupt Request in HALT Mode
Release Source
MK
××
PR
××
IE ISP
Operation
0 0 0
×
Next address instruction execution
0 0 1
×
Interrupt servicing execution
0 1 0 1
0 1
×
0
Next address instruction execution
0 1 1 1
Interrupt
servicing
execution
Maskable interrupt request
1
×
×
×
HALT mode held
RESET input
−
−
×
×
Reset processing
×
: Don’t care
















































