Page 7.12 - 6
COMBIVERT F5-A, -E, -H
© KEB, 2012-10
Posi- and synchronous operating
7.12.2.1
Approach to reference point / modes
There are 3 different Modes of position reference:
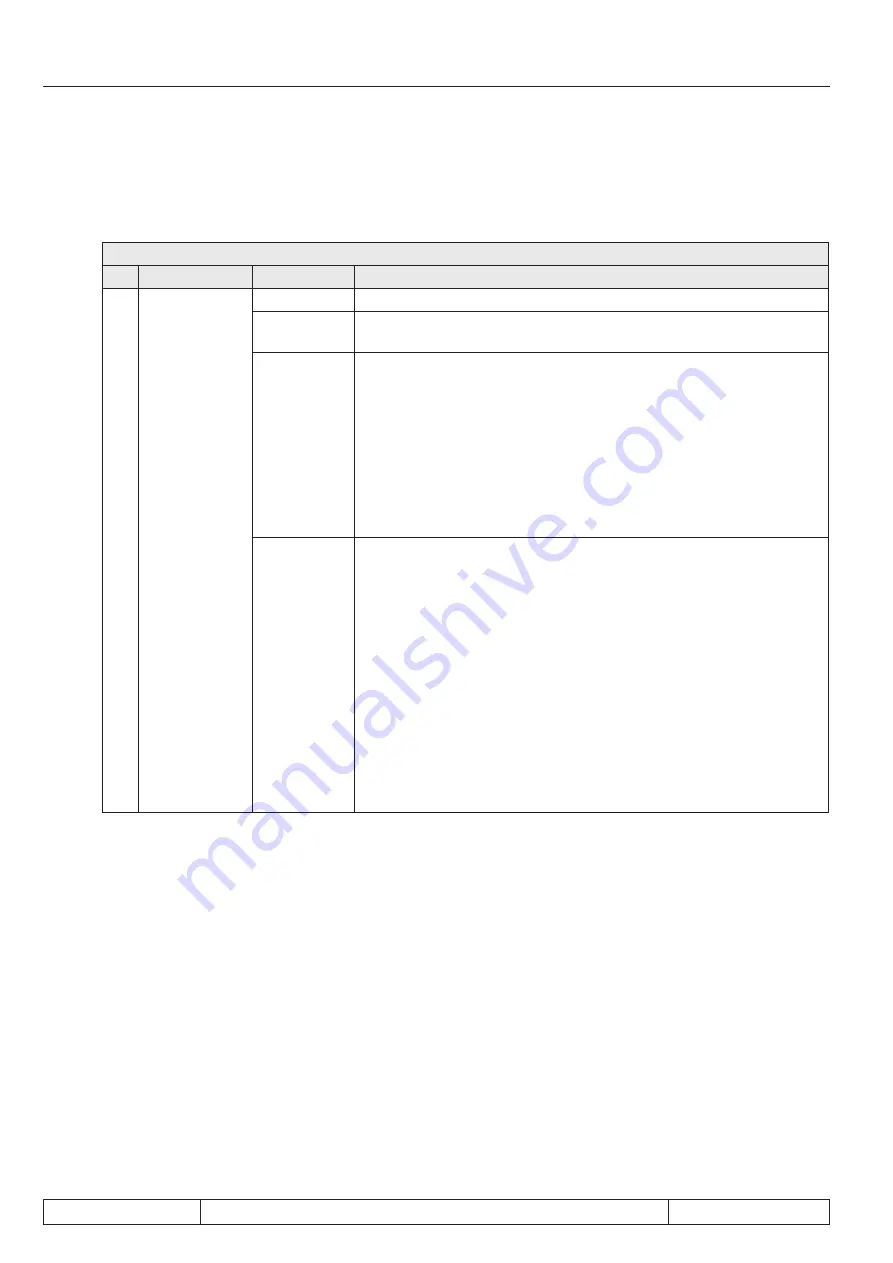
PS.14: Mode of position reference
Bit
Meaning
Value
Explanation
0/1
Mode of positi-
on reference
0: off
No approach to reference point
1: no auto-
start
Approach to reference point is started via digital input. The input is
defined with
PS.19.
2: autostart
The approach to reference point is carried out automatically during
the first "start positioning” command after "power on", even if the po
-
sitioning mode has not been activated yet (input with function "Posi-
tioning /synchronous activation" not set). If the approach to reference
point is interrupted (e.g., by switching off the control release), all
other "start positioning" commands also start an approach to refe-
rence point. Has the reference point search been completed once,
no approach to reference point can be initiated with "start positioning"
anymore. If, additionally, an input is occupied with the function "ap-
proach to reference point", this input is also active.
3: last positi-
on (at power-
on-reset)
The software limit switches are immediately active (if programmed in
Pn.66). The switching condition „approach to reference point com-
pleted“ is met. The value for the actual position (ru.54) is generated
as follows:
●
Encoder without absolute position information (e.g., incremen-
tal encoder)
: After "power on" the actual position is = the last ac-
quired actual position before "power off". To ensure that the position
is correct, the encoder may not turn anymore after power off.
●
Encoder with single-turn absolute position information (e.g.,
resolver)
: After "power on", the position is read out by the encoder
within one revolution, the count of whole revolutions is taken from the
last actual position before "power off". To ensure that the position is
correct, the encoder may turn maximally ½ revolution after power off.
●
Encoder With multi turn absolute position information
:
The current actual position is read from the encoder after "power on".
In mode 1 and 2, the approach to reference point is started on the rising edge of input "start approach to refe-
rence point" (mode 1) and "start positioning" (mode 2), respectively.
The approach to reference point starts with the speed adjusted in PS.21 "reference speed". The direction of
rotation which is used first for the reference point search (the preferred direction f rotation) is
set by the sign
of PS.21 . A positive sign means the drive first looks for the reference point switch in the clockwise direction of
rotation.
The acceleration / deceleration ramps during the approach to reference point are not defined via the OP para
-
meters but via PS.20 "reference acc./dec. time".
Attention: the ramp time and the approach to reference point speed must be chosen so that the drive can stop
and reverse as long as the reference point switch is active. Otherwise, faulty referencing can occur (e.g., stop
on the wrong side of the reference point).
To achieve the most precise referencing, an "approach to reference point free drive-speed" can be programmed
in PS.22. for free driving of the reference switch. If this parameter is set to "0:off", the free drive-speed is taken
as ¼ of the approach to reference point speed (PS.21) .
The actual position is overwritten with the value of PS.17 "reference point" at the reference point.
Summary of Contents for COMBIVERT F5-A
Page 1: ...KEB COMBIVERT F5 A E H 4 4 APPLICATION MANUAL Mat No Rev 00F5AEA K440 1A...
Page 2: ...Page 1 1 2 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2008 02 Table of contents...
Page 4: ...Page 1 1 4 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2008 02 Table of contents...
Page 14: ...Page 1 1 14 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2008 02 Table of contents...
Page 20: ...Page 2 1 6 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2012 10 Product Overview...
Page 28: ...Page 3 1 8 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2012 10 Control Units...
Page 34: ...Page 4 1 6 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2012 10 Fundamentals...
Page 40: ...Page 4 2 6 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2012 10 Password input...
Page 42: ...Page 5 1 2 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2012 10 Selection of Operating Mode...
Page 46: ...Page 5 1 6 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2012 10 Selection of Operating Mode...
Page 70: ...Page 6 2 20 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2012 10 Start up...
Page 140: ...Page 7 3 44 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2012 10 Digital in and outputs...
Page 238: ...Page 7 7 12 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2012 10 Speed control...
Page 254: ...Page 7 8 16 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2012 10 Torque display and limiting...
Page 260: ...Page 7 9 6 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2012 10 Torque control...
Page 292: ...Page 7 11 26 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2012 10 Speed measurement...
Page 432: ...Page 7 14 14 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2012 10 Parameter sets...
Page 466: ...Page 7 15 34 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2012 10 Special functions...
Page 478: ...Page 7 16 12 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2012 10 CP Parameter definition...
Page 488: ...Page 8 1 10 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2012 10 Troubleshooting...
Page 496: ...Page 9 1 8 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2012 10 General design...
Page 538: ...Page 11 1 28 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2012 10 Parameter...
Page 540: ...Page 12 1 2 COMBIVERT F5 A E H KEB 2008 02 Annex 12 1 1 Index 12 1 3...






























