Asterion DC Multioutput ASA Series Operational Manual
M330516-01
2-16
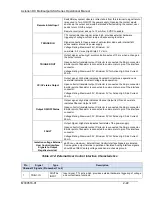
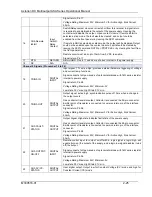
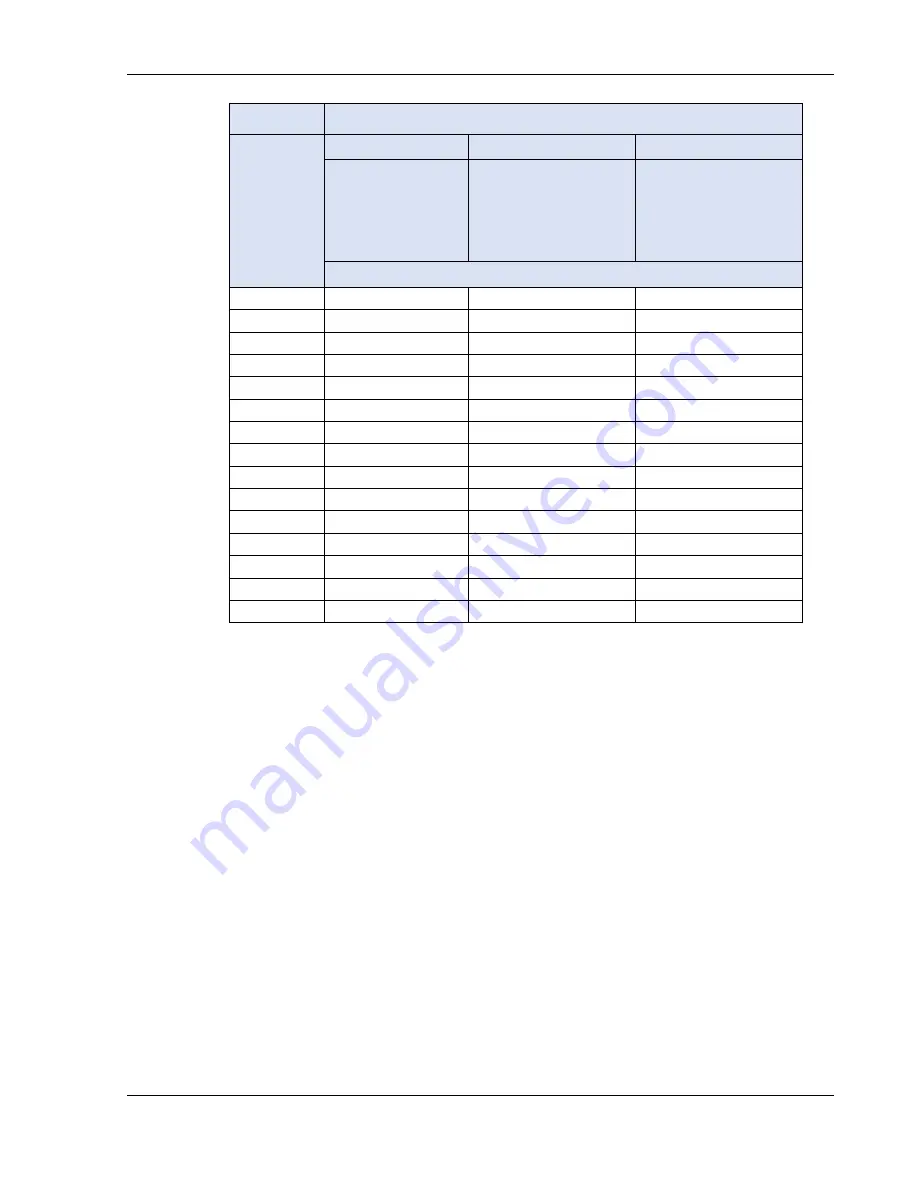
Size
Temperature Rating of Copper Conductor
AWG
60°C
75°C
90°C
Types: TW, UF
Types: RHW, THHW,
THW, THWN, XHHW,
USE, ZW
Types: TBS, SA, SIS,
FEP, FEPB, MI, RHH,
THHN, THHW, XHH,
XHHW
Current Rating, A(RMS)
18
−
−
14
16
−
−
18
14
15
20
25
12
20
25
30
10
30
35
40
8
40
50
55
6
55
65
75
4
70
85
95
3
85
100
115
2
95
115
130
1
110
130
145
0
125
150
170
00
145
175
195
000
165
200
225
0000
195
230
260
Table 2-8: Minimum Wire Size
When determining the optimum cable specification for your power applications, the
same engineering rules apply whether at the input or output of an electrical device.
Therefore, this guide applies equally to the input cable and output cable for this power
source and application loads.
Power cables must be able to safely carry maximum load current without overheating
or causing insulation degradation. It is important to power source performance to
minimize IR (voltage drop) loss within the cable. These losses have a direct effect on
the quality of power delivered to and from the power source and corresponding loads.
When specifying wire gauge, consider derating due to operating temperature at the
wire location. Wire gauge current capability and insulation performance drops with the
increased temperature developed within a cable bundle and with increased
environmental temperature. Therefore, short cables with derating of gauge size and
insulation properties are recommended for power source applications.
Be careful when using published commercial utility wiring codes. These codes are
designed for the internal wiring of homes and buildings and accommodate the safety
factors of wiring loss, heat, breakdown insulation, aging, etc. However, these codes
consider that up to 5% voltage drop is acceptable. Such a loss directly detracts from
the performance specifications of this power source. Also, consider how the wiring
codes apply to bundles of wire within a cable arrangement.