Functions
6-72
7SA522 Manual
C53000-G1176-C119-2
6.3
Measures to Be Taken in Case of Power Swings
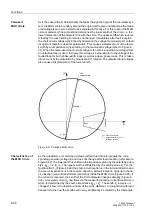
Following dynamic events such as load jumps, short-circuits, reclose dead times or
switching actions it is possible that the generators must realign themselves, in an os-
cillatory manner, with the new load balance of the system. The distance protection
registers large transient currents during the power swing and, especially at the electri-
cal centre, small voltages (Figure 6-40). Small voltages with simultaneous large cur-
rents apparently imply small impedances, which again could lead to tripping by the dis-
tance protection. In expansive networks with large transferred power, even the stabil-
ity of the energy transfer could be endangered by such power swings.
Figure 6-40 Power swing
To avoid uncontrolled tripping, the distance protection devices are supplemented with
power swing blocking functions. At particular locations in the system, out-of-step trip-
ping devices are also applied to split the system into islanded networks at selected lo-
cations, when system stability (synchronism) is lost due to severe (unstable) power
swings.
The 7SA522 has an integrated power swing supplement which allows both the block-
ing of trips by the distance protection during power swings (power swing blocking) and
the calculated tripping during unstable power swings (out-of-step tripping).
6.3.1
Method of Operation
Detection of
Power Swings
System power swings are three phase symmetrical processes. Therefore in general a
certain degree of measured value symmetry may be assumed. System power swings
may however also occur during unsymmetrical processes, e.g. during two-phase
short-circuits or during single-pole dead times. The power swing detection in the
7SA522 is therefore based on three measuring systems. For each phase, a dedicated
measuring system is available. Even if a power swing has been detected, any short-
circuits that may occur during this period result in the fast cancellation of the power
swing block in the affected phases, thereby allowing the tripping of the distance pro-
tection.
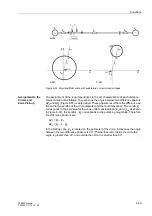
To detect a power swing, the rate of change of the impedance vector is measured. In
the case of the polygon characteristic, the measurement is started when the imped-
ance vector enters the power swing measuring range PPOL (refer to Figure 6-41). The
fault detection range APOL is made up of the largest set values for R and X of all the
activated zones. The power swing range has a minimum distance Z
diff
of 5
Ω
(at I
N
=
M
E
2
E
1
M
E
2
E
1
I
U
E
2
E
1
M
U
Z
1
Z
2
I
at the measuring location M
I
E
1
E
2
–
Z
1
Z
2
+
-------------------
=
Содержание siprotec 7SA522
Страница 20: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Страница 64: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Страница 89: ...SIPROTEC 4 Devices 4 25 7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 Figure 4 20 CFC Logic example ...
Страница 408: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Страница 456: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Страница 516: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Страница 620: ...Appendix B 48 ...