4. STARTUP
4 - 8
4.2.6 Trouble at start-up
CAUTION
Never make a drastic adjustment or change to the parameter values as doing so
will make the operation unstable.
POINT
Using the optional MR Configurator2, you can refer to reason for rotation failure,
etc.
The following faults may occur at start-up. If any of such faults occurs, take the corresponding action.
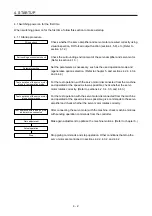
(1) Troubleshooting
No. Start-up
sequence
Fault
Investigation Possible
cause
Reference
1 Power
on
7-segment LED is
not lit.
7-segment LED
blinks.
Not improved even if CN1 and
CN2 connectors are disconnected.
1. Power supply voltage fault
2. The servo amplifier is
malfunctioning.
Improved when CN1 connector is
disconnected.
Power supply of CN1 cabling is
shorted.
Improved when CN2 connector is
disconnected.
1. Power supply of encoder
cabling is shorted.
2. Encoder is malfunctioning.
Alarm occurs.
Refer to chapter 8 and remove cause.
Chapter 8
2
Switch on SON
(Servo-on).
Alarm occurs.
Refer to chapter 8 and remove cause.
Chapter 8
Servo motor shaft is
not servo-locked.
(Servo motor shaft is
free.)
1. Check the display to see if the
servo amplifier is ready to
operate.
2. Check the external I/O signal
indication (section 4.5.7) to see
if SON (Servo-on) is on.
1. SON (Servo-on) is not input.
(wiring mistake)
2. 24 V DC power is not
supplied to DICOM.
Section
4.5.7
3 Input
command
pulse (test
operation).
Servo motor does not
rotate.
Check the cumulative command
pulse on the status display
(section 4.5.3).
1. Wiring mistake
(a) For open collector pulse
train input, 24 V DC power
is not supplied to OPC.
(b) LSP and LSN are not on.
2. Pulse is not input from the
controller.
Section
4.5.3
Mistake in setting of [Pr. PA13].
Chapter
5
Servo motor run in
reverse direction.
1. Mistake in wiring to controller.
2. Mistake in setting of [Pr.
PA14].
4 Gain
adjustment Rotation ripples (speed
fluctuations) are large
at low speed.
Make gain adjustment in the
following procedure.
1. Increase the auto tuning
response level.
2. Repeat acceleration and
deceleration three times to
complete auto tuning.
Gain adjustment fault
Chapter
6
Large load inertia
moment causes the
servo motor shaft to
oscillate side to side.
If the servo motor may be driven
with safety, repeat acceleration
and deceleration three times to
complete auto tuning.
Gain adjustment fault
Chapter
6
5
Cyclic operation
Position shift occurs
Confirm the cumulative command
pulses, cumulative feedback
pulses and actual servo motor
position.
Pulse counting error, etc. due to
noise.
(2) in
this
section
Содержание MR-JE-_A
Страница 9: ...A 8 MEMO ...
Страница 15: ...6 MEMO ...
Страница 29: ...1 FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1 14 MEMO ...
Страница 139: ...4 STARTUP 4 38 MEMO ...
Страница 187: ...5 PARAMETERS 5 48 MEMO ...
Страница 221: ...6 NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 34 MEMO ...
Страница 259: ...8 TROUBLESHOOTING 8 8 MEMO ...
Страница 264: ...9 DIMENSIONS 9 5 2 SCR connector system 3M Receptacle 36210 0100PL Shell kit 36310 3200 008 Unit mm 34 8 39 5 22 4 11 0 ...
Страница 265: ...9 DIMENSIONS 9 6 MEMO ...
Страница 273: ...10 CHARACTERISTICS 10 8 MEMO ...
Страница 339: ...12 COMMUNICATION FUNCTION MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC GENERAL PURPOSE AC SERVO PROTOCOL 12 34 MEMO ...