Chapter 12 Troubleshooting
11
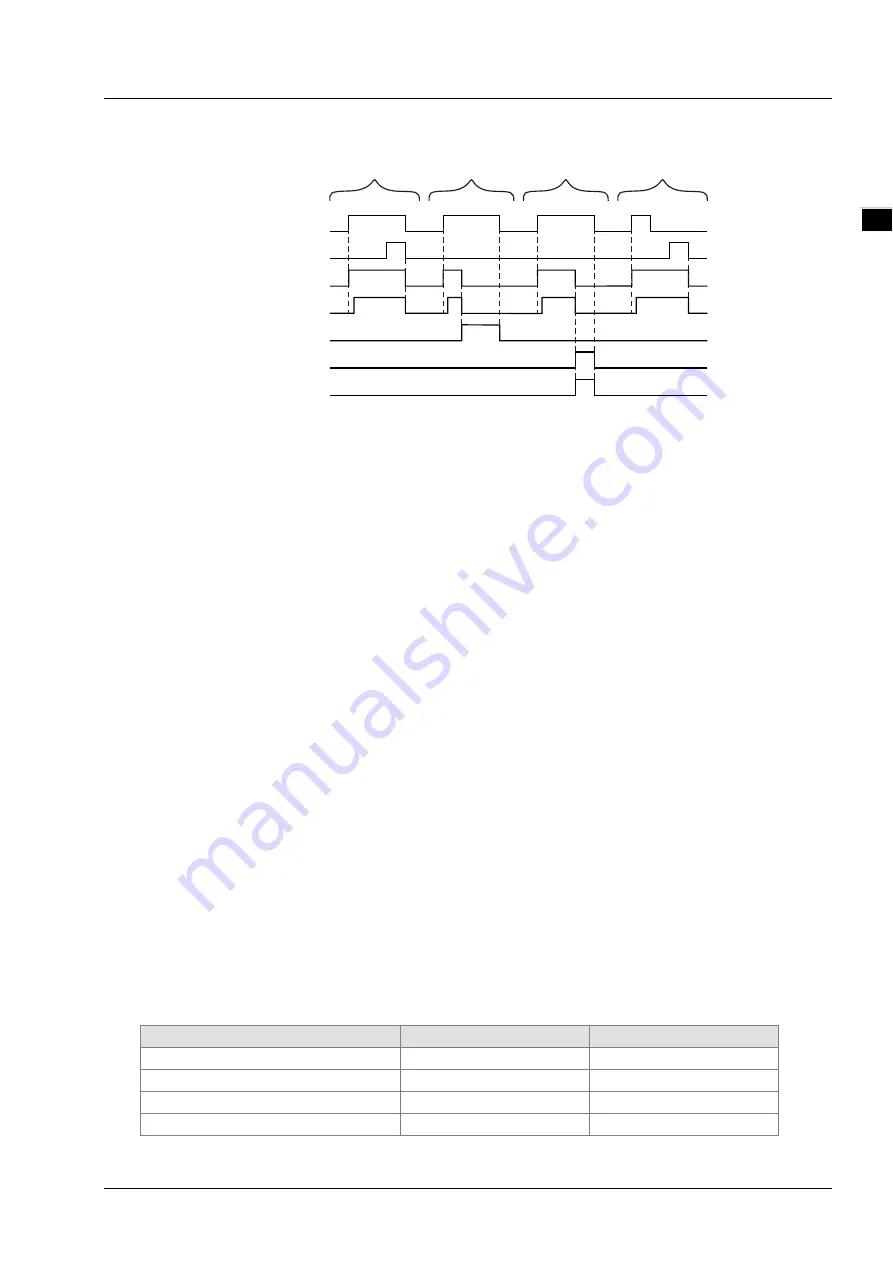
Output Update Timing Chart
Case 1
:
When
Execute
changes from FALSE to TRUE,
Busy
changes to TRUE and one period
later,
Active
changes to TRUE. When the deceleration ends and the axis speed is
decreased to 0,
Done
changes to TRUE and
Busy
and
Active
remain TRUE.
Case 2
:
When the MC_Stop instruction is aborted by another MC_Stop instruction after
Execute
changes from FALSE to TRUE,
CommandAborted
changes to TRUE and meanwhile
Busy
and
Active
change to FALSE. When
Execute
changes from TRUE to FALSE,
CommandAborted
changes to FALSE.
Case 3
:
When an error occurs such as axis alarm or Offline after
Execute
changes from FALSE to
TRUE,
Error
changes to TRUE and
ErrorID
shows the corresponding error code. And
Meanwhile,
Busy
and
Active
change to FALSE.
Error
changes to FALSE when
Execute
changes from TRUE to FALSE.
Case 4
:
In the course of execution of the instruction,
Done
changes to TRUE and
Busy
and
Active
remain TRUE when the instruction execution is completed after
Execute
changes from
TRUE to FALSE. One period later,
Done,
Busy
and
Active
all
change to FALSE.
Function
MC_Stop is used to make the axis decrease its speed at a given deceleration rate till it stops.
As long as
Execute
is TRUE after execution of MC_Stop is completed and the axis velocity is
decreased to 0, the axis state will be in the Stopping state all the time. And during that period, other
motion instruction can not be executed.
If there are two MC_Stop instructions in the program for controlling the same axis, the previously
being executed MC_Stop will be aborted by the later executed MC_Stop instruction.
Compared to MC_Halt instruction, MC_Stop instruction will make the axis locked and thus the
controller cannot perform other motion instruction excluding MC_Stop during MC_Stop execution.
The controller still cannot perform other motion instructions when the execution of MC_Stop is
finished and the axis has stopped. Other motion instruction can not be executed until
Execute
of
MC_Stop changes from TRUE to FALSE.
Programming Example 1
The example of MC_Stop execution is shown as below.
1.
The variable table and program
Variable name
Data type
Initial value
Pwr
MC_Power
Axis1
USINT
1
Pwr_En
BOOL
FALSE
Pwr_BM
MC_Buffer_Mode
0
Ex ec ute
Done
B usy
Ac tive
Co mma ndAbo rt ed
Error
Case 1
Cas e 2
Case 3
Cas e 4
Error I D
11-33
Содержание DVP15MC11T
Страница 9: ...Memo viii...
Страница 15: ...DVP15MC11T Operation Manual _2 MEMO 2 4...
Страница 71: ...DVP15MC11T Operation Manual _7 Memo 7 10...
Страница 81: ...DVP15MC11T Operation Manual _8 Timing Chart F_TRG_CLK F_TRG_Q 8 10...
Страница 158: ...Chapter 8 Logic Instructions 8_ The program 1 ASIN EN ENO In Out ASIN_EN ASIN_In Out1 8 87...
Страница 213: ...DVP15MC11T Operation Manual _8 The program 1 LIMIT EN ENO MN Out MX In LIMIT_EN LIMIT_MN LIMIT_MX LIMIT_In Out1 8 142...
Страница 216: ...Chapter 8 Logic Instructions 8_ The program 1 BAND EN ENO MN Out MX In BAND_EN BAND_MN BAND_MX BAND_In Out1 8 145...
Страница 249: ...DVP15MC11T Operation Manual _8 8 178...
Страница 285: ...DVP15MC11T Operation Manual _8 Memo 8 214...
Страница 286: ...9 Chapter 9 Introductions of Axis Parameters Table of Contents 9 1 Description of Axis Parameters 9 2 9 1...
Страница 323: ...DVP15MC11T Operation Manual 10 MEMO 10 34...
Страница 549: ...DVP15MC11T Operation Manual A MEMO A 16...
Страница 571: ...DVP15MC11T Operation Manual C Memo C 10...
Страница 572: ...D Appendix D Explanation of Homing Modes Table of Contents D 1 Explanation of Homing Modes D 2 D 1...
















































