V04.00 | 2021/05
57
8.4
Configuring devices at PROFINET
8.4.1
PROFINET IO device model
The technical properties of PROFINET IO devices are defined via their device description file, the
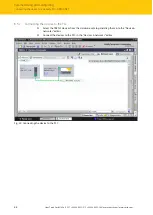
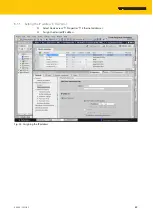
GSDML file. A PROFINET IO device consists of 1…n slots, which can also contain 1…n sub slots.
Sub slots are placeholders for sub modules and establish the interface to the process. Sub mod-
ules can contain parameters, data and diagnostics.
Slot 0 is always reserved as Device Access Point (DAP). The DAP contains the physical interface
to the Ethernet network and represents the device. The other slots and sub slots represent the
other device functions. The structure is defined by the manufacturer of field devices. It is not
necessary that every slot or respectively sub slot is related to physical functions. The allocation
of the slots and sub slots and thus the assignment of functions (operation mode, diagnostics,
etc.) is done in the configuration software of the PROFINET controller. This device model allows
manufacturers to design modular and flexible decentral field devices. Users are flexible in con-
figuring decentralized field devices.
Fig. 47: TIA-Portal – assignment of the slots and sub slots on the example of an TBEN-S1-8DXP
8.4.2
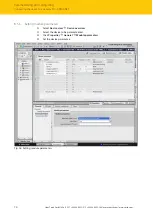
Address setting in PROFINET
In IP-based communication, the field devices are addressed by means of an IP address.
PROFINET uses the Discovery and Configuration Protocol (DCP) for IP assignment.
When delivered, each field device has, among other things, a MAC address. This information is
sufficient to give the respective field device a unique name.
The address is assigned in two steps:
n
Assignment of a unique plant specific name to the respective field device.
n
Assignment of the IP address from the IO-Controller before the system start-up based on the
plant-specific (unique) name.