5-15
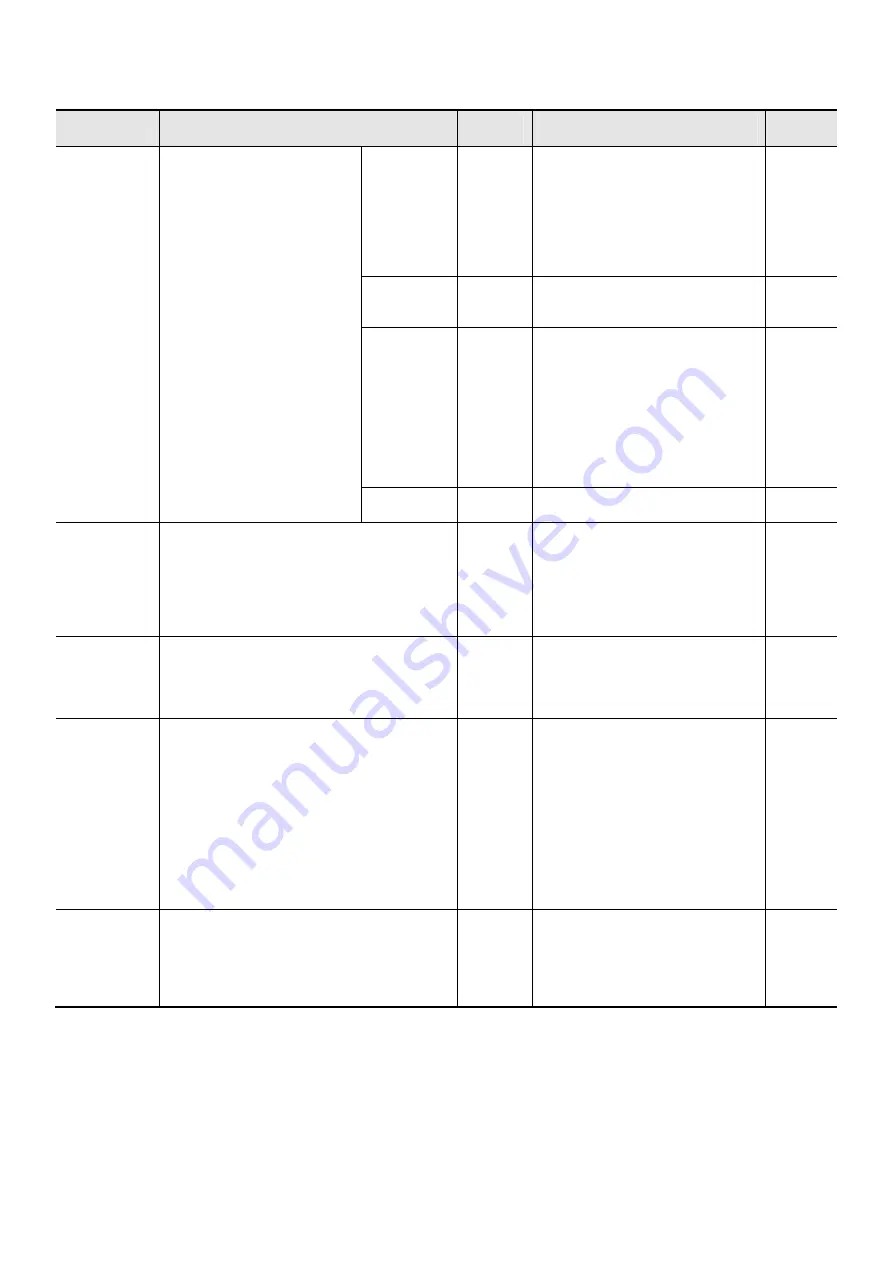
2.6 LIST OF ALARM CODES
Name
Content
Alarm
code
Check content and
countermeasures
Reference
Overcurrent
protection
If the motor is restrained or if it
is put under sudden
acceleration/deceleration,
large amount of current will
flow into the inverter, and may
cause damage. Therefore, the
protection circuit will activate at
approximately 200% of the
inverter rated output current,
and trips.
During
constant
speed
operation
E01.
Are there any sudden changes in
load?
• Decrease the amount of load
changes.
Are there any short-circuits?
• Check the output line.
Are there any ground faults?
• Check the output line and motor.
During
deceleration
E02.
Are there any sudden deceleration?
• Make the deceleration time
longer.
During
acceleration
E03.
Are there any sudden acceleration?
• Make the acceleration time
longer.
Are motor locks observed?
• Check the motor and wiring.
Is the torque boost high?
• Lower the torque boost.
• Is the setting and adjustments of
the motor correct when in PM
motor?
Other E04.
Is the DC control too high?
• Lower the damping force.
Overload
protection
*1
The output current of the inverter is being
monitored, and if the internal electric thermal
detects an overload of the motor, it will trip. If
the overload protection of the motor and
inverter is separated under the settings of the
motor electric thermal function selection (b910),
it will function as a motor overload protection.
E05.
Is there excessive load?
• Lower the load factor.
Is the thermal level (b012/b212)
correct?
• Adjust so that it is correct.
Overload
protection of
the limiting
resistor
Trips when the activity ratio of the regenerative
braking exceeds the activity ratio configured in
b090.
E06.
Are there any sudden deceleration?
• Make the deceleration time
longer.
Is the run cycle too short?
• Make the run cycle longer.
Overcurrent
protection
If the DC current between P/+2 and N/-
becomes too high, it may result in damage.
Therefore, the motor will trip if the DC current
between P/+2, N/- exceeds approximately DC
400V (200 V level)/800 V (400 V level) due to
the rising of regenerative energy or receiving
voltage.
E07.
Are there any sudden deceleration?
• Make the deceleration time
longer.
Are there any ground faults?
• Check the output line and motor.
Is the motor being rotated from the
load side?
• Reduce the regenerative power.
Is the receiving voltage rising?
• Lower the receiving voltage, limit
the power supply variation, use
AC reactor for input.
EEPROM
error
*2
Trips when faults in the internal EEPROM occur
due to abnormal rising of external noise or
temperature. (May result in CPU errors in some
cases.)
E08.
Is there any source of strong noise?
• Take measures for the noise.
Is the cooling efficiency dropping?
• Check the cooling fin for
clogging, and clean.
• Replace cooling fan.
*1: Reset operation will not be available until approximately 10 seconds elapses after the trip (after the protection function
activates).
*2: Reset operation with the RS port or the STOP/RESET key will not be available when errors occur. Turn the machine off once.
If an error occurs when powering on the next time, the memory is damaged, or the parameter has not been saved properly.
Initialize and reconfigure the parameter.
Summary of Contents for MK0003
Page 2: ......
Page 8: ...0 6...
Page 12: ...1 4 2 DIMENSIONAL DRAWING OF OUTRIGGER WIDTH...
Page 17: ...1 9 4 WORKING RADIUS LIFTING HEIGHT...
Page 18: ...1 10 Working range diagram Outrigger extended to maximum Main boom 1 section...
Page 19: ...1 11 Working range diagram Outrigger extended to maximum Main boom 2 sections...
Page 20: ...1 12 Working range diagram Outrigger extended to maximum Main boom 2 5 sections...
Page 21: ...1 13 Working range diagram Outrigger extended to maximum Main boom 3 sections...
Page 22: ...1 14 Working range diagram Outrigger extended to minimum Main boom 1 section...
Page 23: ...1 15 Working range diagram Outrigger extended to minimum Main boom 2 sections...
Page 24: ...1 16 Working range diagram Outrigger extended to minimum Main boom 2 5 sections...
Page 25: ...1 17 Working range diagram Outrigger extended to minimum Main boom 3 sections...
Page 26: ...1 18 5 RATED TOTAL LOAD CHART...
Page 32: ...2 4...
Page 33: ...2 5 1 HYDRAULIC CIRCUIT DIAGRAM 200 1176600...
Page 34: ...2 6...
Page 35: ...2 7 2 HYDRAULIC PIPING DIAGRAM 2 1 CRANE ROTATING PART 200 1171800...
Page 41: ...2 13 2 2 CONTROL LINE A...
Page 43: ...2 15 2 3CONTROL LINE B Perform spiral winding on the entire perimeter of the hose of this part...
Page 45: ...2 17 2 4 TRAVEL LINE...
Page 47: ...2 19 2 5 OUTRIGGER LINE...
Page 49: ...2 21 2 6 PT LINE 102 1152000 4...
Page 69: ...2 41...
Page 70: ...2 42...
Page 71: ...2 43...
Page 76: ...2 48 4 8 ENGINE ACCESSORIES 102 1149200...
Page 90: ...2 62 7 2 INTERNAL STRUCTURE...
Page 120: ...2 92 Part B Writing method for wire number Two places...
Page 123: ...2 95 Figure 1 Index point Figure 2 Connection diagram...
Page 166: ...2 138 15 4 APPEARANCE OF OUTRIGGER ON REAR LEFT SIDE 200 2167300...
Page 173: ...2 145 17 ELECTRIC CIRCUIT DIAGRAM 200 1176500 01...
Page 174: ...2 146 18 ELECTRIC SYSTEM 18 1 1 WIRE HARNESS OF MACHINE BODY 1 200 1172200 1...
Page 176: ...2 148 18 1 2 WIRE HARNESS OF MACHINE BODY 2 200 1172200 2...
Page 179: ...2 151 19 CONTROL ASSEMBLY 19 1 CONTROLLER 1 TTC60 Pin arrangement...
Page 180: ...2 152 TTC60 I O...
Page 181: ...2 153 2 TTC36X Pin arrangement...
Page 182: ...2 154 TTC36X lower part I O...
Page 209: ...2 181 19 2 5 LIST OF CONTROLLER INPUT MONITORING...
Page 210: ...2 182 19 2 6 LIST OF CONTROLLER ANALOG INPUT OUTPUT MONITORING...
Page 245: ...3 9 1 2 3 ANGLE METER 360 S200M3297000...
Page 274: ...3 38...
Page 293: ...4 19 8 SERVICE LOCATIONS...
Page 294: ...4 20...
Page 296: ...5 2 1 ELECTRICAL MOTOR UNIT ASSEMBLY Unit weight 180 kg...
Page 324: ...5 30...
Page 325: ...5 31 4 ELECTRICAL DIAGRAM S200M3122000 01...
Page 326: ...5 32 S200M3122000 02...
Page 336: ...6 8 1 3 2 INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF WINCH MOTOR...
Page 345: ...6 17 4 WORKING RADIUS LIFTING HEIGHT OF ONE FALL WINCH...
Page 348: ......






























