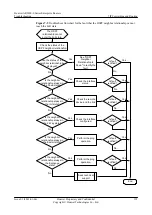
If the metric of a received route exceeds 16, the route is regarded as unreachable and is not added
to the routing table.
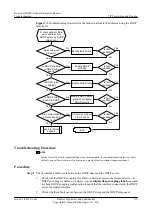
Step 8
Check whether the authentication on the sending and receiving interface is matching.
Run the
display rip
process-id
statistics
interface
interface-type interface-number
command
to check whether packet authentication has failed on the interface.
If the packet authentication was failed on the interface, it must be configured correctly.
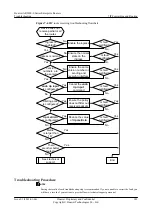
Step 9
Check whether other protocols have learned the same routes in the routing table.
Run the
display rip
process-id
route
command to check whether routes have been received
from the neighbor.
The possible cause is that the RIP route is received correctly and the local device learns the same
route from other protocols such as OSPF and IS-IS.
The weights of OSPF or IS-IS are generally greater than that of RIP. Routes learned through
OSPF or IS-IS are preferred by routing management.
Run the
display ip routing-table protocol
rip
verbose
command to view routes in the Inactive
state.
Step 10
If the fault persists, contact Huawei technical support personnel and provide them with the
following information.
l
Results of the preceding troubleshooting procedure
l
Configuration files, log files, and alarm files of the devices
----End
Relevant Alarms and Logs
Relevant Alarms
None.
Relevant Logs
None.
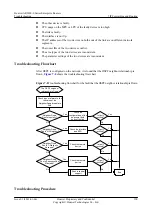
7.3.2 Device Does not Send Some or All Routes
Common Causes
This fault is commonly caused by one of the following:
l
The outgoing interface is not enabled with RIP.
l
The outgoing interface is not in the Up state.
l
The
silent-interface
command is configured on the outgoing interface so that the interface
is suppressed from sending RIP packets.
Huawei AR2200-S Series Enterprise Routers
Troubleshooting
7 IP Forwarding and Routing
Issue 01 (2012-01-06)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
185