218
Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide
53-1001763-02
Logical fabric overview
10
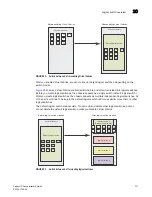
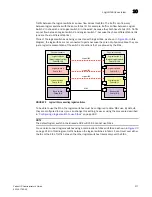
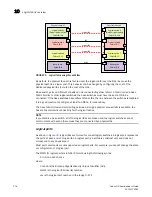
FIGURE 30
Logical fabric using ISLs and XISLs
By default, the physical ISL path is favored over the logical path (over the XISL) because the
physical path has a lower cost. This behavior can be changed by configuring the cost of the
dedicated physical ISL to match the cost of the LISL.
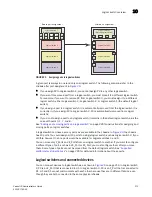
Base switch ports on different chassis can be connected together to form a fabric, called a
base
fabric
. Similar to other logical switches, the base switches must have the same FID to be
connected. If the base switches have different fabric IDs, the link between the switches is disabled.
It is a good practice to configure at least two XISLs, for redundancy.
The base fabric follows normal routing policies. As long as physical connectivity is available, the
base fabric maintains connectivity for the logical fabrics.
NOTE
If you disable a base switch, all of the logical ISLs are broken and the logical switches cannot
communicate with each other unless they are connected by a physical ISL.
Logical ports
As shown in
Figure 30
, logical ISLs are formed to connect logical switches. A
logical port
represents
the ports at each end of a logical ISL. A logical port is a software construct only and does not
correspond to any physical port.
Most port commands are not supported on logical ports. For example, you cannot change the state
or configuration of a logical port.
The WWN for logical ports is in NAA=5 format, using the following syntax:
5
n
:
nn
:
nn
:
nz
:
zz
:
zz
:
z
x:
xx
where:
nnnnnn
is the Brocade Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI).
zzzzzz
is the logical fabric serial number.
xxx
is the logical port number, in the range 0—FFF.
ISL
Base switch
Fabric ID 8
P9
Logical switch 7
Fabric ID 15
P7
Logical switch 6
Fabric ID 1
P4
Physical chassis 2
Base switch
Fabric ID 8
P6
Logical switch 3
Fabric ID 15
P5
Logical switch 2
Fabric ID 1
P2
Physical chassis 1
P8
P6
P2
XISL
Logical ISL
Logical ISL
Logical ISL
Logical switch 5
(Default logical switch)
Fabric ID 128
Logical switch 1
(Default logical switch)
Fabric ID 128
P1
P1
Summary of Contents for 53-1001763-02
Page 1: ...53 1001763 02 13 September 2010 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide Supporting Fabric OS v6 4 0 ...
Page 4: ...iv Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 ...
Page 24: ...xxiv Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 ...
Page 28: ...xxviii Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 ...
Page 32: ...xxxii Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 ...
Page 40: ...xl Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 ...
Page 42: ...2 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 ...
Page 54: ...14 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 High availability of daemon processes 1 ...
Page 74: ...34 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 Basic connections 2 ...
Page 102: ...62 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 Audit log configuration 3 ...
Page 214: ...174 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 Management interface security 7 ...
Page 228: ...188 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 Brocade configuration form 8 ...
Page 276: ...236 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 Creating a logical fabric using XISLs 10 ...
Page 404: ...364 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 ...
Page 440: ...400 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 Performance data collection 17 ...
Page 480: ...440 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 F_Port masterless trunking 19 ...
Page 494: ...454 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 Buffer credit recovery 20 ...
Page 574: ...534 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 Hexadecimal overview E ...