Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide
461
53-1001763-02
Fibre Channel routing concepts
21
Proxy devices
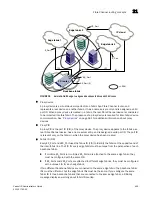
An FC router achieves inter-fabric device connectivity by creating proxy devices (hosts and targets)
in attached fabrics that represent real devices in other fabrics. For example, a host in Fabric 1 can
communicate with a target in Fabric 2 as follows:
•
A proxy target in Fabric 1 represents the real target in Fabric 2.
•
Likewise, a proxy host in Fabric 2 represents the real host in Fabric 1.
The host discovers and sends Fibre Channel frames to the proxy target. The FC router receives
these frames, translates them appropriately, then delivers them to the destination fabric for
delivery to the target.
The target responds by sending frames to the proxy host. Hosts and targets are exported from the
edge SAN to which they are attached and, correspondingly, imported into the edge SAN reached
through Fibre Channel routing.
Figure 71
illustrates this concept.
FIGURE 71
MetaSAN with imported devices
Routing types
The FC-FC routing service provides two types of routing:
•
Edge-to-Edge
Occurs when devices in one edge fabric communicate with devices in another edge fabric
through one or more FC routers.
•
Backbone-to-Edge
Occurs when FC routers connect to a common fabric—known as a backbone fabric—through
E_Ports. A backbone fabric can be used as a transport fabric that interconnects edge fabrics.
FC routers also enable hosts and targets in edge fabrics to communicate with devices in the
backbone fabric, known as
backbone-to-edge routing
. From the edge fabric's perspective, the
backbone fabric is just like any other edge fabric. For the edge fabric and backbone fabric
devices to communicate, the shared devices must be presented to each other's native fabric.
Host
Target
Fabric 1
Fabric 2
FC router
E_Port
E_Port
IFL
IFL
EX_Port
Proxy host
(imported device)
Proxy target
(imported device)
Summary of Contents for 53-1001763-02
Page 1: ...53 1001763 02 13 September 2010 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide Supporting Fabric OS v6 4 0 ...
Page 4: ...iv Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 ...
Page 24: ...xxiv Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 ...
Page 28: ...xxviii Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 ...
Page 32: ...xxxii Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 ...
Page 40: ...xl Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 ...
Page 42: ...2 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 ...
Page 54: ...14 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 High availability of daemon processes 1 ...
Page 74: ...34 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 Basic connections 2 ...
Page 102: ...62 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 Audit log configuration 3 ...
Page 214: ...174 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 Management interface security 7 ...
Page 228: ...188 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 Brocade configuration form 8 ...
Page 276: ...236 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 Creating a logical fabric using XISLs 10 ...
Page 404: ...364 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 ...
Page 440: ...400 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 Performance data collection 17 ...
Page 480: ...440 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 F_Port masterless trunking 19 ...
Page 494: ...454 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 Buffer credit recovery 20 ...
Page 574: ...534 Fabric OS Administrator s Guide 53 1001763 02 Hexadecimal overview E ...