Functional Description
ARM DDI 0500D
Copyright © 2013-2014 ARM. All rights reserved.
2-11
ID021414
Non-Confidential
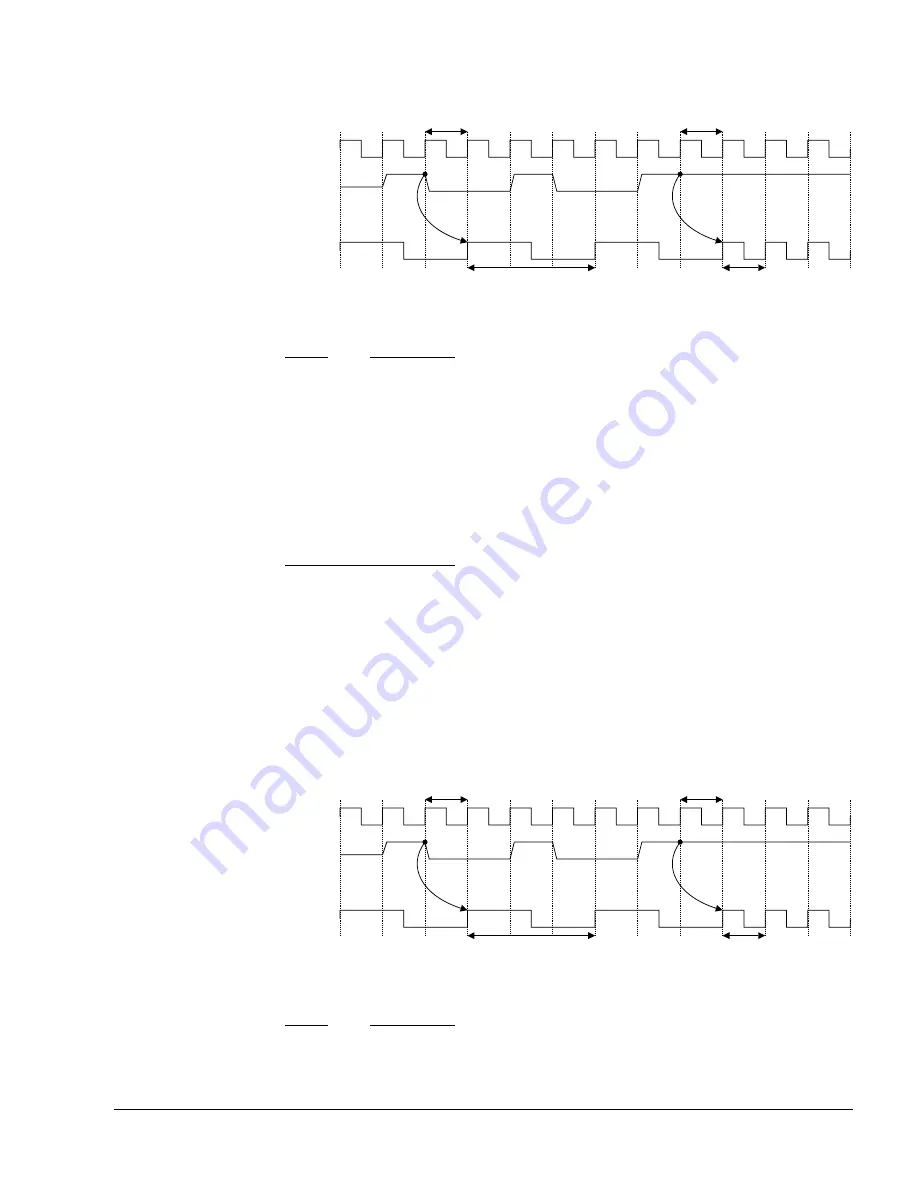
Figure 2-4 ACLKENS with CLKIN:ACLKS ratio changing from 3:1 to 1:1
Note
•
Figure 2-4
shows the timing relationship between the AXI slave clock,
ACLKS
and
ACLKENS
, where
ACLKENS
asserts one clock cycle before the rising edge of
ACLKS
. It is important that the relationship between
ACLKS
and
ACLKENS
is
maintained.
•
If there are any physical effects that could occur while changing the clock frequency,
ARM recommends that the clock ratio is changed only while the
STANDBYWFIL2
output of the processor is asserted.
•
The input signal
ACLKENS
exists in the Cortex-A53 processor if it is configured to
include the ACP interface.
SCLKEN
This signal is present only if the master interface is configured to use the CHI protocol. The SCU
interface supports integer ratios of the
CLKIN
frequency, for example 1:1, 2:1, 3:1. These
ratios are configured through external clock enable signals. In all cases CHI transfers remain
synchronous. The CHI master interface includes the
SCLKEN
clock enable signal.
Figure 2-5
shows a timing example of
SCLKEN
that changes the
CLKIN
to
SCLK
frequency
ratio from 3:1 to 1:1.
Figure 2-5 SCLKEN with CLKIN:SCLK ratio changing from 3:1 to 1:1
Note
•
Figure 2-5
shows the timing relationship between the CHI clock,
SCLK
and
SCLKEN
,
where
SCLKEN
asserts one
CLKIN
cycle before the rising edge of
SCLK
. It is
important that the relationship between
SCLK
and
SCLKEN
is maintained.
ACLKS
ACLKENS
asserts one
CLKIN
cycle before the rising edge of
ACLKS
1
CLKIN
cycle
CLKIN
:
ACLKS
= 3:1
CLKIN
:
ACLKS
= 1:1
ACLKENS
CLKIN
1
CLKIN
cycle
SCLK
SCLKEN
asserts one
CLKIN
cycle
before the rising edge of
SCLK
1
CLKIN
cycle
CLKIN
:
SCLK
= 3:1
CLKIN
:
SCLK
= 1:1
SCLKEN
CLKIN
1
CLKIN
cycle
















































