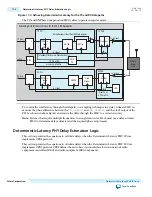
Figure 11-2: Achieving Deterministic Latency for the TX and RX Datapaths
The TX and RX Phase Compensation FIFOs always operate in register mode.
TX Data
RX Data
bitslipboundaryselect (from RX Word Aligner)
TX PMA
tx_dataout
D
Q
D
Q
Serializer
RX PMA
De-
serializer
CMU
PLL
GPLL
CDR
refclk
refclk
(from On- or
Off-Chip PLL)
<n>
8B/10B
rx_datain
RX PC S
TX PC S
Achieving Deterministic Latency for the TX & RX Datapaths
RX Phase
Comp
FIFO
TX Phase
Comp
FIFO
tx_clkout
TX PLL refclk
or External refclk Pin
TX Feedback (for Remote Radio Head Only)
rx_clkout
8B/10B
Word
Aligner
Bit Slip
Remote
Radio
Head
To control the total latency through the datapath, use sampling techniques in a delay estimate FIFO to
measure the phase difference between the
tx_clkout
and
rx_clkout
, and the clock output of the
PLL (as shown in above figure) and ensure the delay through the FIFO to a certain accuracy.
Note: Systems that require multiple frequencies in a single transceiver block must use a delay estimate
FIFO to determine delay estimates and the required phase adjustments.
Deterministic Latency PHY Delay Estimation Logic
This section provides the equations to calculate delays when the Deterministic Latency PHY IP core
implements CPRI protocol.
This section provides the equations to calculate delays when the Deterministic Latency PHY IP Core
implements CPRI protocol. CPRI defines the radio base station interface between network radio
equipment controllers (REC) and radio equipment (RE) components.
11-4
Deterministic Latency PHY Delay Estimation Logic
UG-01080
2015.01.19
Altera Corporation
Deterministic Latency PHY IP Core
Send Feedback