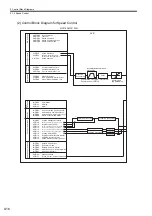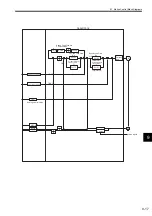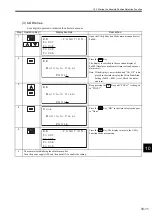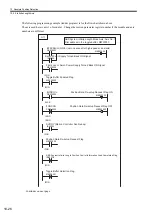
10 Absolute Position Detection
10.3.1 Finite Length Axis
10-12
10.3 Using an Absolute Encoder
This section explains precautions regarding use as well as the procedure for setting the zero point when using an
absolute encoder.
10.3.1 Finite Length Axis
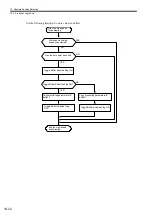
(1) Overview
An absolute encoder stores the multiturn data in internal memory backed up by battery. This way the zero point
of the coordinate system can be determined without the zero point return operation when the system is started up.
Once the system is started, the encoder functions just like an incremental encoder.
Unfortunately, the maximum multiturn data is
±
99999 for the
Σ
Series and -32768 to 32767 for the
Σ
-II /III
Series. If system power is turned ON when the multiturn data exceeds these limits, the MP2100/MP2100M posi-
tion will not be the same before and after power is turned ON.
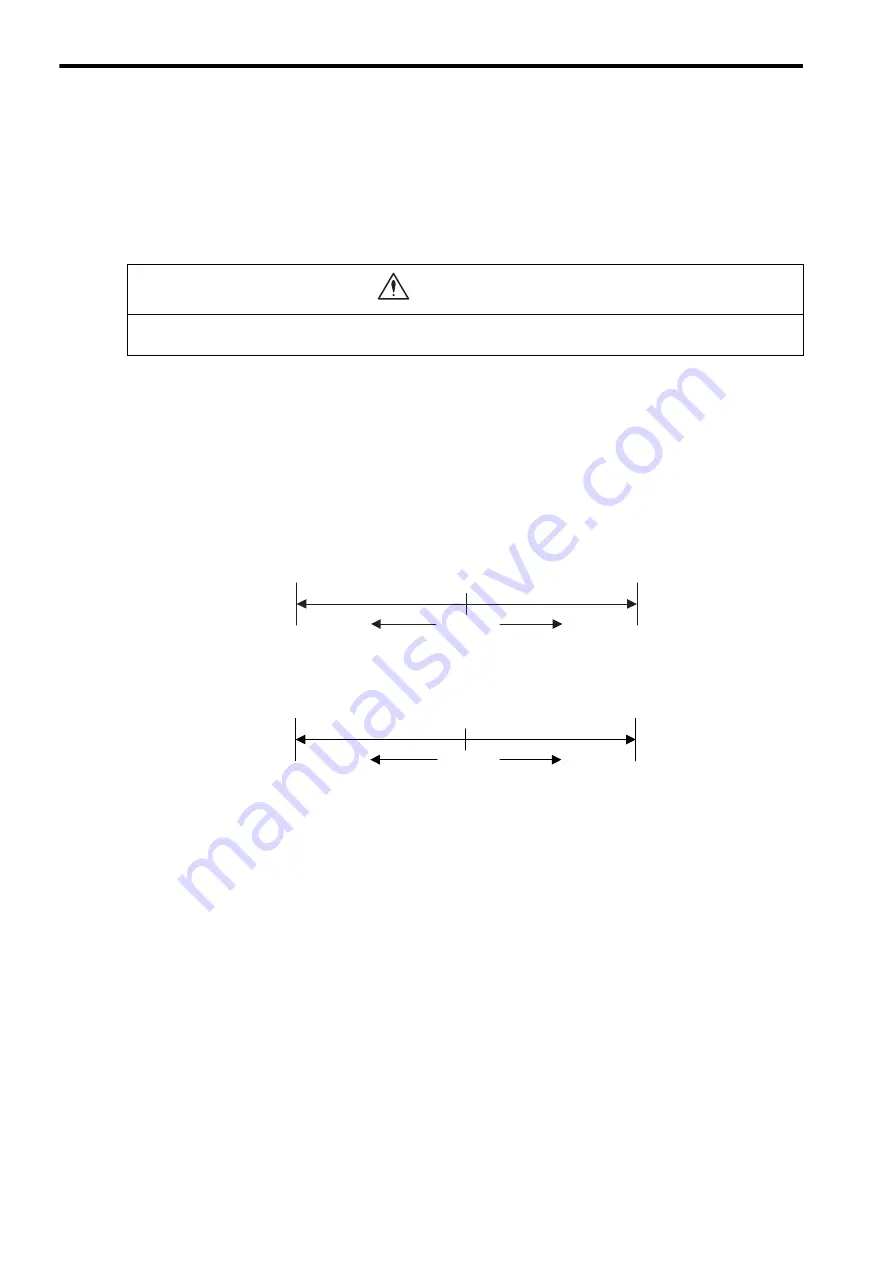
The multiturn data for the encoder functions as illustrated below.
(a)
Σ
Series
(b)
Σ
-
II
or
Σ
-
III
Series
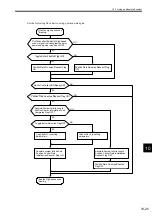
Therefore, be sure to observe the following precautions when using an absolute encoder for a finite length
axis.
• Be sure to initialize the encoder prior to setting the zero point.
• Use the absolute encoder within the range of the multiturn data.
Note: The actual machine operating range may vary depending on parameters like the gear ratio.
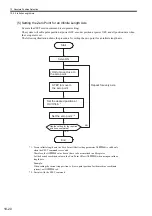
(2) Position
Management with a Finite Length Axis
Initialize the axis position as described next when power is turned ON if an absolute encoder is used for a finite
length axis.
• Current position for the machine coordinate system = Encoder position when servo power is turned ON
*
+
Zero Point Offset (setting parameter OL
48)
* The encoder position when servo power is turned ON is as follows:
Multiturn data
×
Number of encoder pulses
+
initial increment pulses.
Refer to your SERVOPACK manual for information on the initial increment pulses.
• Do not change the Zero Point Offset (OL
48) while operating a machine with a finite length axis.
Otherwise the machine may be damaged or an accident may occur.
CAUTION
Reverse limit
Forward limit
Reference
position
Reverse
direction
Forward
direction
0
(
−
99999 rotations)
(+99999 rotations)
Reverse limit
Forward limit
Reverse
direction
Forward
direction
0
(
−
32768 rotations)
(+32767 rotations)
Reference
position