13.1 Overview of Troubleshooting
13-3
13
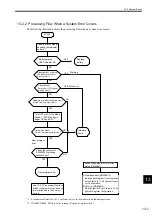
13.1.2 Basic Troubleshooting Flow
When a problem occurs, it is important to determine the cause and treat the problem fast to get the system up and
running as quickly as possible. The following table shows the basic troubleshooting flow.
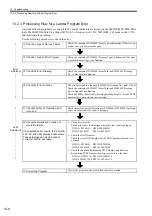
13.1.3 Indicator Errors
Error details can be checked by the status of indicators on the front of the MP2100/MP2100M Module.
In the process, we narrow down the repair location in a program by getting an overview of the error from indica-
tors, checking the contents of the system (S) registers, examining the drawing or function number that caused the
error and then getting an overview of operation error details.
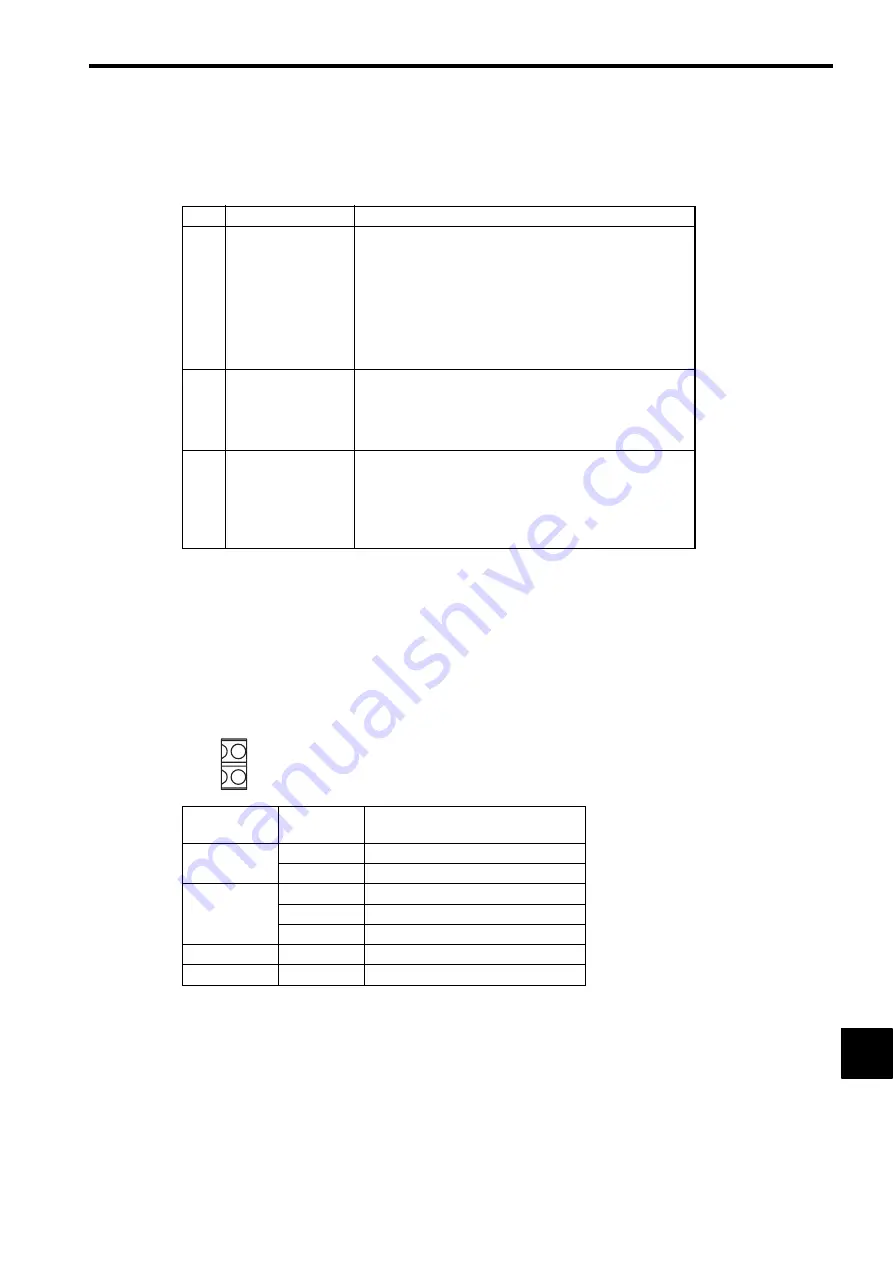
(1) Indicators
The following indicators show operating status and error details for the MP2100/MP2100M.
No.
Point
Basic Details Examined
1
Visual Check
• Equipment operation (status while stopped)
• Power ON/OFF
• I/O equipment status
• Wiring status
• Status of indicators
• Status of all switches (mode switches and other switches)
• Parameters and program content check
2
Error Check
Observe whether the following alters the error in any way.
• Stopping the MP2100/MP2100M.
• Resetting the alarm.
• Turning power OFF and ON.
3
Narrowing the
Range
Consider possible failure locations based on the results of 1
and 2 above.
• Is the problem in the MP2100/MP2100M or external?
• Is the problem in sequence control or motion control?
• Is the problem software or hardware?
Indicator
Name
Indicator
Color
Significance When Lit
S1
Green
Lights for normal operation.
Red
Lights/blinks for failures.
S2
Not lit
User program stopping.
Green
Lights for normal operation.
Red
Lights/blinks for warning.
TX
Green
Data is being sent to M-I/II.
BAT
Red
Battery alarm occurred.
BAT
TX
S2
S1