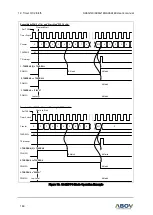
15. USI
A96G140/A96G148/A96A148 User’s manual
160
15.3
USIn clock generation
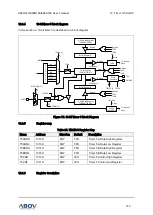
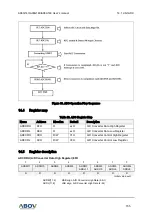
Figure 85. Clock Generation Block Diagram (USIn)
Clock generation logic generates base clock signal for the transmitter and the receiver. The USIn
supports four modes of clock operation such as normal asynchronous mode, double speed
asynchronous mode, master synchronous mode and slave synchronous mode.
The clock generation scheme for master SPI mode and slave SPI mode is the same as master
synchronous and slave synchronous operation mode. The USInMS[1:0] bits in USInCR1 register
selects one from asynchronous operation and synchronous operation. Asynchronous double speed
mode is controlled by the DBLSn bit in the USInCR2 register. The MASTERn bit in USInCR3 register
controls whether the clock source is internal (master mode, output pin) or external (slave mode, input
pin). The SCKn pin is active only when the USIn operates in synchronous or SPI mode.
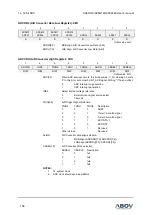
Table 29 shows the equations for calculating the baud rate (in bps).
Table 29. Equations for Calculating USIn Baud Rate Register Setting
Operating Mode
Equation for Calculating Baud Rate
Asynchronous Normal Mode (DBLSn=0)
Baud Rate =
fx
16( 1)
Asynchronous Double Speed Mode (DBLSn=1)
Baud Rate =
fx
8( 1)
Synchronous or SPI Master Mode
Baud Rate =
fx
2( 1)