14. 12-bit ADC
A96G140/A96G148/A96A148 User’s manual
152
14
12-bit ADC
Analog-to-digital converter (ADC) of A96G140/A96G148/A96A148 allows conversion of an analog input
signal to corresponding 12-bit digital value. This A/D module has eight analog inputs. Output of the
multiplexer becomes input into the converter which generates the result through successive
approximation.
The A/D module has four registers which are the A/D converter control high register (ADCCRH), A/D
converter control low register (ADCCRL), A/D converter data high register (ADCDRH), and A/D
converter data low register (ADCDRL).
ADSEL[3:0] bits are used to select channels to be converted. To execute A/D conversion, TRIG[2:0]
bits should be set to ‘xxx’. Registers ADCDRH and ADCDRL contain the result of A/D conversion. When
the conversion is completed, the result is loaded into ADCDRH and ADCDRL, A/D conversion status
b
it AFLAG is set to ‘1’, and A/D interrupt is set. During the A/D conversion, AFLAG bit is read as ‘0’.
14.1
Conversion timing
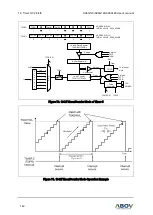
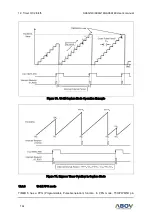
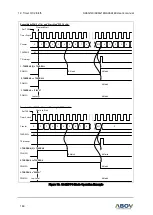
A/D conversion process requires 4 steps (4 clock edges) to convert each bit and 12 clocks to set up
A/D conversion. Therefore, total of 58 clocks are required to complete a 12-bit conversion: For example,
when fxx/8 is selected for conversion clock with a 12MHz fxx clock frequency, one clock cycle is 0.66μs,
and each bit conversion requires 4 clocks. The conversion rate is calculated as follows:
4 clocks/bit × 12 bits + set
-up time = 60 clocks
ADC Conversion Time = ADCLK * 60 cycles
Please remember that the A/D converter requires at least 7.5us for conversion time, so the conversion
time must be set bigger than 7.5us.
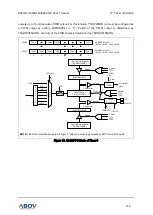
14.2
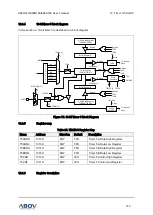
Block diagram
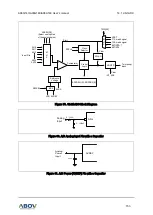
In this section, the 12-bit ADC is described in a block diagram, and an analog input pin and a power pin
with capacitors respectively are introduced.