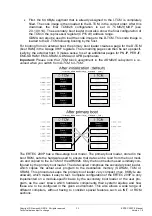
Copyright © Siemens AG 2016. All rights reserved
44
ERTEC 200P-2 Manual
Technical data subject to change
Version 1.0
Requirements
Processor frequency
125/250 MHz
AHB frequency
125 MHz
AHB width
32 bit
AHB bus access width
8/16/32 bit
APB bus frequency
125 MHz
APB bus width
32 bit
APB bus access width
8/16/32 bit
Table 5: Internal bus system, parameters of internal buses
2.3.2.2 Endianness
The ERTEC 200P operates with little endianness.
No
endian swappers are available at
the AHB interfaces.
2.3.2.3 AHB Subsystem (Multi-Layer AHB)
The multi-layer AHB bus is a 32-bit bus with multi-master capability. It runs at 125 MHz
and has the functionality of the ARM-AHB Lite bus (see document /11/, see chapter 7.2)
connecting multiple AHB segments in a multi-layer AHB allows 7 AHB masters to access
different slaves simultaneously.
An arbiter decides which master is to be assigned a given slave when multiple masters
access the slave simultaneously.
A retry functionality is not implemented at the AHB in the light of the multi-layer architec-
ture (AHB-Lite). Split functionality is not supported either (AHB-Lite).
Alongside Okay and Error, Split and Retry are also ways to acknowledge an AHB transfer
from the slave. Retry response indicates that the transfer is not yet complete and that the
master should repeat the transfer. Split response indicates that the transfer has not yet
been successfully completed. The master must release the bus and cannot be reas-
signed the bus until the slave indicates to the bus arbiter that it is able to complete an
AHB transfer. The master must repeat the transfer for this purpose.
The lock function can be enabled for the ARM master (ARM926-D) in the SCRB register
M_LOCK_CTRL. Default setting: lock functionality is disabled. The ARM926-I master
cannot generate a lock.
Definition of AHB-Lite bus
AHB-Lite:
A subset of the full AMBA AHB protocol specification. It provides all of the
basic functions required by the majority of AMBA AHB slave and master designs, particu-
larly when used with a multi-layer AMBA interconnect. In most cases, the extra facilities
provided by a full AMBA AHB interface are implemented more efficiently by using an
AMBA AXI protocol interface.
More detailed documentation is available at: /11/ AHB_Lite_Protocol
.