151
Intera 5.3
Information for Integrators
Risk assessment
Sawyer is supplied for assembly with other equipment to form a complete machine and is not itself
a complete machine. Integrators must therefore perform an application risk assessment based on
general shop safety rules and safety standards that considers the installation, surroundings, work-
force training and competence, and the general safety culture. The purpose of the risk assessment
is to ensure that hazards posed to users are eliminated or minimized in accordance with occupa-
tional health & safety requirements established by local regulatory authorities. Guidance on the risk
assessment process may be found in the following standards (non-exhaustive):
•
ISO 10218-2:2011 Robots and robotic devices - Safety requirements - Part 2:
Industrial robot systems and integration
•
RIA TR R15.306-2014 Technical Report for Industrial Robots and Robot Systems
- Safety Requirements, Task-based Risk Assessment Methodology.
•
ISO 12100:2010 Safety of machinery - General principles for design - Risk
assessment and risk reduction
•
ANSI B11.0-2010 Safety of Machinery; General Requirements & Risk Assess-
ment.
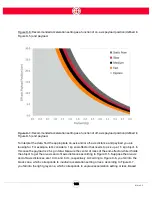
The risk assessment shall take into account all potential contact between an operator and the robot
during normal use and foreseeable misuse. The operator's neck, face and head shall not be
exposed to contact.
The risks associated with collaborative operation of Sawyer are reduced to levels as low as reason-
ably practicable through a combination of inherently safe design measures employed by Rethink
Robotics and safe practices/risk assessments carried out by integrators and end users. Any resid-
ual risks remaining with the robot prior to installation are communicated to integrators and end
users through this document. If the integrator’s risk assessment for the specific application deter-
mines there is an unacceptable level of risk, additional risk reduction measures must be applied.
Summary of Contents for Sawyer
Page 15: ...8 Intera 5 3 Getting to Know Sawyer Hardware Overview of Your Robot ...
Page 16: ...9 Intera 5 3 Getting to Know Sawyer Dimensions ...
Page 17: ...10 Intera 5 3 Getting to Know Sawyer Sawyer Reach ...
Page 93: ...86 Intera 5 3 Train Pick and Place Patterns on the Head 11 Press OK to go to the next step ...
Page 104: ...97 Intera 5 3 Train Pick and Place Patterns on the Head You may now run the task ...
Page 134: ...127 Intera 5 3 TCP IP The Set To node in the Behavior Editor is used to output information ...
Page 138: ...131 Intera 5 3 Fieldbus Devices 3 Using a keyboard navigate to CONFIGURATION and press ENTER ...
Page 155: ...148 Intera 5 3 ...
Page 156: ...149 Intera 5 3 ...
Page 180: ...173 Intera 5 3 ...
Page 190: ...183 Intera 5 3 Fixed Data 112 From Robot ...
Page 206: ...199 Intera 5 3 Small Assembly 114 From Robot 115 To Robot ...
Page 207: ...200 Intera 5 3 Large Assembly 116 From Robot 117 To Robot ...
Page 208: ...201 Intera 5 3 Floats 118 From Robot 119 To Robot ...
Page 209: ...202 Intera 5 3 Strings 120 From Robot 121 To Robot ...
Page 218: ...Z Zero G button 16 17 Zero G mode 24 Zero Gravity mode 17 zoom reset 42 ...
Page 219: ......
Page 220: ...Last updated June 18 2018 Intera 5 3 User Guide Getting Started Rev A ...