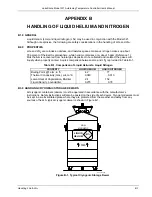
Lake Shore Model 321 Autotuning Temperature Controller User’s Manual
Glossary of Terminology
A-7
remanence
. The remaining magnetic induction in a magnetic material when the material is first saturated and then the
applied field is reduced to zero. The remanence would be the upper limit to values for the remanent induction. Note
that no strict convention exists for the use of remanent induction and remanence and in some contexts the two terms
may be used interchangeably.
remanent induction
. The remaining magnetic induction in a magnetic material after an applied field is reduced to zero.
Also
see
remanence.
repeatability
. The closeness of agreement among repeated measurements of the same variable under the same
conditions.
2
resistance temperature detector (RTD)
. Resistive sensors whose electrical resistance is a known function of the
temperature, made of, e.g., carbon-glass, germanium, platinum, or rhodium-iron.
resolution
. The degree to which nearly equal values of a quantity can be discriminated.
2
display resolution
. The resolution of an instrument's physical display. This is not always the same as the
measurement resolution of the instrument. Decimal display resolution specified as "n digits" has 10
n
possible
display values. A resolution of n and one-half digits has 2 x 10
n
possible values.
measurement resolution
. The ability of an instrument to resolve a measured quantity. For digital instrumentation
this is often defined by the analog to digital converter being used. A n-bit converter can resolve one part in 2
n
.
The smallest signal change that can be measured is the full scale input divided by 2
n
for any given range.
Resolution should not be confused with accuracy.
RhFe
. Rhodium-iron. Rhodium alloyed with less than one atomic percent iron is used to make the Lake Shore RF family
of sensors. Rhodium-iron is a spin fluctuation alloy which has a significant temperature coefficient of resistance below
20 K where most metals rapidly lose sensitivity.
RJ-11
. A modular connector with 6 conductors commonly used with telephones.
Roman numerals
. Letters employed in the ancient Roman system of numeration as follows:
I
1 VI
6 L
50
II
2 VII
7 C
100
III
3 VIII
8 D
500
IV 4
IX 9
M
1000
V 5
X 10
root mean square (RMS)
. The square root of the time average of the square of a quantity; for a periodic quantity the
average is taken over one complete cycle. Also known as effective value.
1
room temperature compensation
. Thermocouples are a differential measurement device. Their signal represents
the difference in temperature between their ends. An ice bath is often used to reference the measurement end to
0 degrees Celsius so most curves are normalized to that temperature. Room temperature compensation replaces an
ice bath by monitoring the temperature of the thermocouple's terminals and normalizing the reading mathematically.
RS-232C
. Bi-directional computer serial interface standard defined by the Electronic Industries Association (EIA). The
interface is single-ended and non-addressable.
Seebeck effect
. The development of a voltage due to differences in temperature between two junctions of dissimilar
metals in the same circuit.
1
self-heating
. Heating of a device due to dissipation of power resulting from the excitation applied to the device. The
output signal from a sensor increases with excitation level, but so does the self-heating and the associated
temperature measurement error.
sensitivity
. The ratio of the response or change induced in the output to a stimulus or change in the input. Temperature
sensitivity of a resistance temperature detector is expressed as S = dR/dT.
setpoint
. The value selected to be maintained by an automatic controller.
1
serial interface
. A computer interface where information is transferred one bit at a time rather than one byte (character)
at a time as in a parallel interface. RS-232C is the most common serial interface.
SI
. Système International d'Unités.
See
International System of Units.
silicon diode
. Temperature sensor based on the forward voltage drop at constant current through a pn semiconductor
junction formed in crystalline silicon.
SoftCal™
. In Lake Shore instruments, SoftCal™ is used to improve the accuracy of a DT-400 Series Silicon Temperature
Diode Sensor. This reduces the error between the sensor and the Standard Curve 10 used by the instrument to
convert input voltage from the diode to a corresponding temperature.
stability
. The ability of an instrument or sensor to maintain a constant output given a constant input.
strain relief
. A predetermined amount of slack to relieve tension in component or lead wires. Also called stress relief.
superconducting magnet
. An electromagnet whose coils are made of a type II superconductor with a high transition
temperature and extremely high critical field, such as niobium-tin, Nb
3
Sn; it is capable of generating magnetic fields of
100,000 oersteds and more with no steady power dissipation.
1
See
electromagnet.