Lake Shore Model 321 Autotuning Temperature Controller User’s Manual
Glossary of Terminology
A-5
line regulation
. The maximum steady-state amount that the output voltage or current will change as the result of a
specified change in input line voltage (usually for a step change between 105
–
125 or 210
–
250 volts, unless
otherwise specified).
line voltage
. The RMS voltage of the primary power source to an instrument.
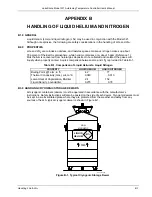
liquid helium (LHe)
. Used for low temperature and superconductivity research: minimum purity 99.998%. Boiling point at
1 atm = 4.2 K. Latent heat of vaporization = 2.6 kilojoules per liter. Liquid density = 0.125 kilograms per liter.
EPA Hazard Categories: Immediate (Acute)
DOT Label: Nonflammable Gas
Health and Sudden Release of Pressure Hazards
DOT Class: Nonflammable Gas
DOT Name: Helium, Refrigerated Liquid
DOT ID No.: UN 1963
liquid nitrogen (LN
2
)
. Also used for low temperature and superconductivity research and for its refrigeration properties
such as in freezing tissue cultures: minimum purity 99.998%, O
2
8 ppm max. Boiling point at 1 atm = 77.4 K. Latent
heat of vaporization = 160 kilojoules per liter. Liquid density = 0.81 kilograms per liter.
EPA Hazard Categories: Immediate (Acute)
DOT Label: Nonflammable Gas
Health and Sudden Release of Pressure Hazards
DOT Class: Nonflammable Gas
DOT Name: Nitrogen, Refrigerated Liquid
DOT ID No.: UN 1977
load regulation
. A steady-state decrease of the value of the specified variable resulting from a specified increase in load,
generally from no-load to full-load unless otherwise specified.
LSCI
. Lake Shore Cryotronics, Inc.
M
. Symbol for magnetization.
See
magnetization.
magnetic air gap
. The air space, or non-magnetic portion, of a magnetic circuit.
magnetic field strength (H)
. The magnetizing force generated by currents and magnetic poles. For most applications,
the magnetic field strength can be thought of as the applied field generated, for example, by a superconducting
magnet. The magnetic field strength is not a property of materials. Measure in SI units of A/m or cgs units of oersted.
magnetic flux density (B)
. Also referred to as magnetic induction. This is the net magnetic response of a medium to an
applied field, H. The relationship is given by the following equation: B = µ
0
(H + M) for SI, and B = H + 4
π
M for cgs,
where H = magnetic field strength, M = magnetization, and µ
0
= permeability of free space = 4
π
x 10
–7
H/m.
magnetic hysteresis
. The property of a magnetic material where the magnetic induction (B) for a given magnetic field
strength (H) depends upon the past history of the samples magnetization.
magnetic induction (B)
.
See
magnetic flux density.
magnetic moment (m)
. This is the fundamental magnetic property measured with dc magnetic measurements systems
such as a vibrating sample magnetometer, extraction magnetometer, SQUID magnetometer, etc. The exact technical
definition relates to the torque exerted on a magnetized sample when placed in a magnetic field. Note that the
moment is a total attribute of a sample and alone does not necessarily supply sufficient information in understanding
material properties. A small highly magnetic sample can have exactly the same moment as a larger weakly magnetic
sample (
see
Magnetization). Measured in SI units as A·m
2
and in cgs units as emu. 1 emu = 10
–3
A·m
2
.
magnetic units
. Units used in measuring magnetic quantities. Includes ampere-turn, gauss, gilbert, line of force, maxwell,
oersted, and unit magnetic pole.
magnetization (M)
. This is a material specific property defined as the magnetic moment (m) per unit volume (V).
M = m/V. Measured in SI units as A/m and in cgs units as emu/cm
3
. 1 emu/cm
3
= 10
3
A/m.
Since the mass of a sample is generally much easier to determine than the volume, magnetization is often alternately
expressed as a mass magnetization defined as the moment per unit mass.
material safety data sheet (MSDS)
. OSHA Form 20 contains descriptive information on hazardous chemicals under
OSHA’s Hazard Communication Standard (HCS). These data sheets also provide precautionary information on the
safe handling of the gas as well as emergency and first aid procedures.
microcontroller
. A microcomputer, microprocessor, or other equipment used for precise process control in data handling,
communication, and manufacturing.
1
MKSA System of Units
. A system in which the basic units are the meter, kilogram, and second, and the ampere is a
derived unit defined by assigning the magnitude 4
π
x 10
–7
to the rationalized magnetic constant (sometimes called
the permeability of space).
NBS
. National Bureau of Standards. Now referred to as NIST.
NbTi
. Niobium-titanium. A superconductive alloy with a transition temperature typically near 9 K in zero magnetic field.
negative temperature coefficient (NTC)
. Refers to the sign of the temperature sensitivity. For example, the resistance of
a NTC sensor decreases with increasing temperature.
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
. Government agency located in Gaithersburg, Maryland and
Boulder, Colorado, that defines measurement standards in the United States.
noise
(electrical). Unwanted electrical signals that produce undesirable effects in circuits of control systems in which they
occur.
2