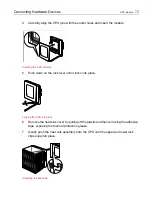
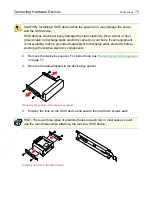
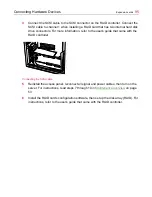
Connecting Hardware Devices
Hard disk drives (HDDs)
84
Hard disk drives (HDDs)
The server drive carrier contains six drive bays. Each bay is assigned a unique SCSI
address. If you have a pedestal model Toshiba Magnia 3200 server, starting with the left
drive bay, the SCSI IDs are assigned as follows:
❖
Bay 1 = SCSI ID 0
❖
Bay 2 = SCSI ID 1
❖
Bay 3 = SCSI ID 2
❖
Bay 4 = SCSI ID 3
❖
Bay 5 = SCSI ID 4
❖
Bay 6 = SCSI ID 5
If you have a rack model Toshiba Magnia 3200 server, hard disk drive Bay 1 (SCSI ID 0)
is the top bay in the drive cage.
When adding a hard disk drive to the server, always position the drive(s) sequentially,
beginning with the first vacant drive bay with the lowest available SCSI ID.
Downgraded server operation
If your server is equipped with a RAID controller for data redundancy and one of the hard
disk drives in the array fails, the system will go into a "downgraded operational state" and
continue to run.
The MegaRAID
®
controller installed in Toshiba Magnia 3200 servers supports the
following standard RAID levels:
❖
RAID 0 (Striping)
❖
RAID 1 (Disk Mirroring)
❖
RAID 5 (Disk Striping with Distributed Parity)
RAID 0 - Disk Striping
Striping, also referred to as a Stripe set, chains multiple drives into a single logical
storage unit. Striping partitions each drive’s storage space into stripes, or data chunks,
which may be as small as one sector (512 bytes) or a large as several megabytes. The
stripes are interleaved so that the combined storage space of the array comprises
alternate stripes from each hard disk drive. The end result is an even distribution storage
space across the entire set of drives in the array.
The type of operating system installed on the server determines whether large or small
stripes are used in the array. Though disk striping utilizes full the I/O capability of the
Summary of Contents for 3200
Page 1: ... ...
Page 309: ...309 ...