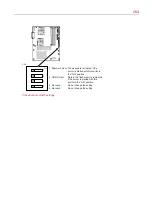
278
application: A computer program that you use to perform tasks of a specific type.
Applications include word processors, spreadsheets and database
management systems. See also program.
array: 1) A table of values that a program treats as a single unit. 2) A set of hard disk
drives that are linked together to provide a very large amount of data storage.
asynchronous: A type of data transmission in which information is sent at variable time
intervals. To indicate when a transmitted character begins and ends, it is
preceded by a start bit and followed by an optional parity bit and one or two
stop bits. See also synchronous.
audio: Audio (sound) frequencies for multimedia systems range from 15 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
Audio includes voice, music, sound effects, and ambient sound.
audio mixing: Creating a custom audio track from several different sources using a
sound-mixing device.
audio stream: Frames of compressed audio.
authoring: The process of writing, editing, and assembling a multimedia program on a
personal computer using a multimedia authoring program.
authoring program: A software development environment used to create multimedia
applications that reduce complex instructions to simple user tasks such as
menu selection, mouse manipulation or typing. Such programs enable
communicators to develop interactive courseware or presentations on
personal computers without extensive programming knowledge.
AUTOEXEC.BAT: A batch file containing MS-DOS commands that the computer
performs every time you start or restart it. For example, it contains commands
that load the Windows operating system. See also batch file.
AVI (Audio Video Interleaved): Microsoft Corporation’s trade name for synchronization
and digital compression of video and audio signals.
Summary of Contents for 3200
Page 1: ... ...
Page 309: ...309 ...