2-12
*1 Install a recommended molded case circuit breaker (MCCB) or residual-current-operated protective device
(RCD)/earth leakage circuit breaker (ELCB) (with overcurrent protection function) in the primary circuit of the
inverter to protect wiring. Ensure that the circuit breaker capacity is equivalent to or lower than the recommended
capacity.
*2 Install a magnetic contactor (MC) for each inverter to separate the inverter from the power supply, apart from the
MCCB or RCD/ELCB, when necessary.
Connect a surge absorber in parallel when installing a coil such as the MC or solenoid near the inverter.
*3 The R0 and T0 terminals are provided for inverters with a capacity of 2 HP or above.
To retain an alarm output signal
ALM
issued on inverter's programmable output terminals by the protective function
or to keep the keypad alive even if the main power has shut down, connect these terminals to the power supply
lines. Without power supply to these terminals, the inverter can run.
*4 Normally no need to be connected. Use these terminals when the inverter is equipped with a high power-factor,
regenerative PWM converter (RHC series).
*5 When connecting an optional DC reactor (DCR), remove the jumper bar from the terminals P1 and P(+).
EQ7-2100-C/EQ7-4100-C and larger HP models require a DCR (packed with the EQ7) to be connected.
Use a DCR when the capacity of the power supply transformer exceeds 500 kVA and is 10 times or more the
inverter rated capacity, or when there are thyristor-driven loads in the same power supply line.
*6 EQ7-2015-C/EQ7-4015-C and smaller have a built-in braking resistor (DBR) between the terminals P(+) and DB.
When connecting an external braking resistor (DBR), be sure to disconnect the built-in one.
*7 A grounding terminal for a motor. Use this terminal if needed.
*8 For control signal wires, use twisted or shielded-twisted wires. When using shielded-twisted wires, connect the
shield of them to the common terminals of the control circuit. To prevent malfunction due to noise, keep the control
circuit wiring away from the main circuit wiring as far as possible (recommended: 10 cm/3.9 inches or more). Never
install them in the same wire duct. When crossing the control circuit wiring with the main circuit wiring, set them at
right angles.
*9 The connection diagram shows factory default functions assigned to digital input terminals [X1] to [X7], [FWD] and
[REV], transistor output terminals [Y1] to [Y4], and relay contact output terminals [Y5A/C] and [30A/B/C].
*10 Switching connectors in the main circuits. For details, refer to "Instruction manual section 2.3.4
Switching
connectors" later in this section.
*11 Slide switches on the control printed circuit board (control PCB). Use these switches to customize the inverter
operations. For details, refer to Section 2.3.6 "Setting up the slide switches."
*12 When the Enable input function is not to be used, keep terminals [EN1]-[PLC] and terminals [EN2]-[PLC]
short-circuited using jumper wires. For opening and closing the hardware circuit between terminals [EN1] and [PLC]
and between [EN2] and [PLC], use safety components such as safety relays and safety switches that comply with
EN954-1 or EN ISO13849-1 Category 3 or higher.
*13 To bring the inverter into compliance with the European Standard, Low Voltage Directive EN61800-5-1, be sure to
insert the specified fuse in the primary circuit of the inverter.
Primary grounding terminal ( G) for inverter enclosure
Two grounding terminals ( G) are not exclusive to the power supply wiring (primary circuit) or motor wiring (secondary
circuit). Be sure to ground either of the two grounding terminals for safety and noise reduction. The inverter is designed
for use with safety grounding to avoid electric shock, fire and other disasters.
The grounding terminal for inverter enclosure should be grounded as follows:
1) Ground the inverter in compliance with the national or local electric code.
2) Use a thick grounding wire with a large surface area and keep the wiring length as short as possible.
Inverter output terminals U, V, and W and secondary grounding terminals ( G) for motor
Inverter’s output terminals should be connected as follows:
1) Connect the three wires of the 3-phase motor to terminals U, V, and W, aligning the phases each other.
2) Connect the secondary grounding wire to the grounding terminal ( G).
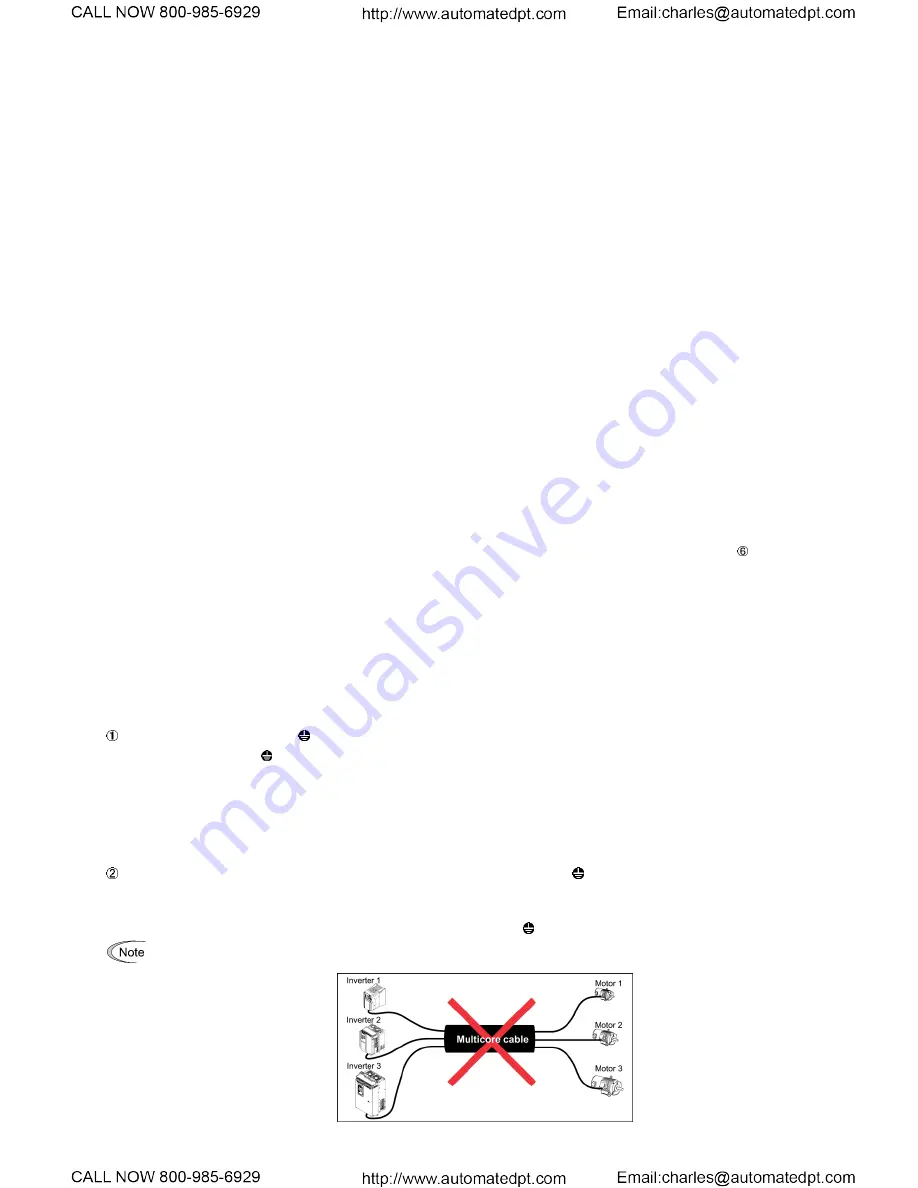
When there is more than one combination of an inverter and motor, do not use a multi-conductor cable for the
purpose of running the leads together.
















































