18 – 4
Section 18
•
Auxiliary Input / Output
Vission 20/20 • Operation and Service Manual • Emerson • 35391SC 2.7
• Low Trip:
•
Defines the lower limit of the input value that
when exceeded will generate a trip.
• High Trip:
•
Defines the upper limit of the input value that
when exceeded will generate a trip.
• Delay:
•
Defines the time period for which input val
-
ue is checked with alarm/trip setpoints before
showing alarm or trip. If the input value is con-
tinuously above or below the alarm or trip set-
points, only then an alarm or trip is generated.
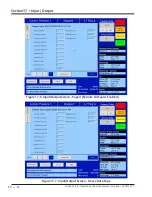
Analog Outputs
This screen gives the ability to map any standard analog
input or auxiliary input to any of the four analog auxiliary
outputs. There are two pages of auxiliary output con-
figuration; each consists of two analog auxiliary outputs.
For Auxiliary Outputs Screens, see Figures 18-6 and 18-7.
• Active Input:
• The active Input can be selected from the
available standard analog inputs or auxiliary in-
puts. The selected Active Input gets mapped to
auxiliary output.
• Run Always:
• “Run Always” option can be selected to en-
able the mapped auxiliary output irrespective
of the compressor’s run state. If “Run Always” is
not selected then the mapped auxiliary output
is enabled only when the compressor is running.
• Trigger:
•
Trigger configuration is used to enable / dis
-
able an auxiliary output according to the con-
figured trigger input. The trigger input can be
selected from the available standard analog
inputs, auxiliary analog inputs or digital inputs.
Trigger value and differential in combination
with trigger type (“enable if above / On” or “en-
able if below / Off”) enables or disables the aux-
iliary output.
Control
Auxiliary outputs can be PID Controlled or Scalable
Controlled.
PID Control:
P = Proportional (gain):
• Used to adjust the auxiliary output in direct propor-
tion to the difference between the control setpoint
and the active input. The proportional term is a unit-
less quantity and is used for coarse adjustment. This
setpoint should be set to the lowest value that gives
adequate control system response. Increasing the
proportional setting increases the control system’s
sensitivity to small process fluctuations and the ten
-
dency to hunt.
I = Integral (reset):
• Used to integrate the error over time, to account for
a small error that has persisted for a long time. This
quantity is used for fine adjustment. This setpoint is
used to smooth out process variations. This setpoint
should be set high enough to prevent hunting but
not too high or it will cause control system overshoot.
D = Derivative (rate):
• Used to account for how fast the error is changing,
positively or negatively.
Setpoint :
• Setpoint used by PID engine.
Inverse:
• This option is used to inverse an Analog Aux Output ,
to vary its output from 20 mA to 4 mA. Typically used
where normally open solenoids are to be operated.
Negative Error:
• The negative Error option is used when PID should be
active only if a negative error is present (Setpoint is
greater than Process Variable).
Scalable Control:
• Minimum Input / Maximum Input:
•
These setpoints define minimum and maxi
-
mum Input range for a configured active input .
• Minimum Output / Maximum Output:
•
These setpoints define minimum and maxi
-
mum output. The Auxiliary output produces a
linear value based on these settings.
Summary of Contents for Vilter Vission 20/20
Page 1: ...Vission 20 20TM Micro controller Operation and service manual Version 2 7 ...
Page 2: ......
Page 4: ......
Page 220: ...B 2 Blank Vission 20 20 Operation and Service Manual Emerson 35391SC 2 7 ...
Page 300: ...D 2 Blank Vission 20 20 Operation and Service Manual Emerson 35391SC 2 6 ...
Page 336: ......
Page 337: ......