Group
28
Ignition
systems
Design
and
function
- Overview
Review of electronic
ignition
systems - II
(Type EZ-K and Rex-I)
A
B
C
0
E
F
G
H
EZ-
102K
EZ-
117K
EZ-
118K
EZ-
115K
EZ-
116K
REX-
I
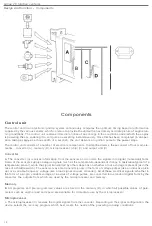
The illustration shows the main components of type
EZ
-
K and Aex-I
ignition
systems
.
Common features
:
An abbreviation of the German term Elektronischer Zundung m
i
t K
lo
pfregulung
(roughly,
'
Electronic
ignition
with
knock sensor
')
the designat
io
n EZ
-
K describes a
group of systems
manufactured by the Bosch
company.
The various
systems
i
n
the
EZ
-
K group are relat
i
vely similar
i
n terms
of
functions and
components.
All feature microprocessor
control and
inco
rporate
a memory which is programmed with a
family
of ideal
timing
curves
for
the
particular en-
gine.
Each
system also includes a sensor which detec
t
s engine
knock
and retards the ignition in
respon
se
to
a
mem
-
ory
program which is
indiv
idu
al
to
each cylinder. This means that
the
timing in each cylinder
may
vary at any given
instant.
As
column
E
indicates,
systems
i
n this group are normally
supplied
w
i
th
engine load information
by an air mass
meter located
in
the
in
take
system.
A measure
of
the quantity
of
air supplied to the engine
,
the a
i
r mass meter
signal
is transmitted to the LH-Jetron
ic
control
un
i
t
(in
which
it is converted
and
used
to
determine
the quantity of fuel to
be
injected) and then to the
ignition system control
un
i
t
.
Differences
Within
the EZ
-K
group,
the
individual systems are distinguished by
t
he
timing curves used for different engine
var
-
iants, by
whether
a
Hall
generator
or
inductive
speed/
position
pick-up is used, and by when
the
ignition compensa-
tion functions
are activated.
6