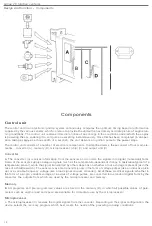
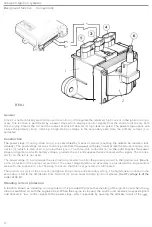
Group
28
Igni
r
ion
sysrems
Design and function
-
Compensation functions
Compensation functions
c
Il
1/
B
A
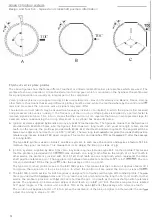
Theory of knock
Knock is
caused
by de
t
onation
of
the
fuel/air mixture in the
combustion chamber.
What
is
knock
Detonation
may occur either aher las
in
A
lar
before
(as in
51
the
has delivered a spark.
either case,
the
ture
i
s
ignited
at two
or
more points
in
the
chamber
and
combustion progresses
from these po
i
nts
Ie).
Th
is
in
the simultaneous propagat
io
n
of
two
or
more flame fronts
,
causing abnormally
rap
i
d and uncontrolled
combus
tion,
accompanied by an explosive rise
in
pressure which produces
the
typical, metallic sound
known
as
'
pinking' or
'knoc
k
'
.
'
Compression
'
knock
A
.
In
the
case
i
n wh
ich
knock
occurs aher the
has
delivered
a spark. detonation is
cau
sed by
the
fact
that the
flame front
i
n
i
tiated by the
compresses and
heats the
unignited
m
ix
ture to the
point at
which detonation
is
unavo
i
dable. A relatively high eng
i
ne
load is
requ
i
red to produce this type
of
knock
.
'
Glow ignition
'
knock
B
.
In
the
type
o
f
knock which
occurs
before the plug has delivered
a spark,
detonation
of
the mixture may
be
due
to
incandescent carbon
part
icles
or
gasket edges
,
fou
le
d
spark plugs
or
other
areas
of
the
combustion chamber
which absorb heat
more easily.
I
Th
is
phenomenon
is
sometimes
known as
'g
low
ignition'.)
Effects
of knock
C
.
The
abnormal pressure rise which accompanies
knock
subjects
the piston, gudgeon pin.
co
nnecting
rod, c
r
ank-
shah and
bear
ings
t
o abnormally
high mechanical
stresses
.
Furthe
rmo
re
,
the
t
empera
t
ure
ri
se
caus
ed
by
th
e
phe
-
nomenon
is
so high
t
hat the
cylinder
wall
.
piston and
spark
plug may easily
suffer
damage
,
while the energy con-
tent
of
the fuel
is
poorly
utilized.
The unusual engine resonance
caused
by knock
is
detected by a knock sensor
mounted
on
the
cylinder
block
.
The
sensor signal
i
s transmitted to the
control
unit
.
28