Sentinel V SC and RT Operation Manual
September
2017
EAR-Controlled Technology Subject to Restrictions Contained on the Cover Page.
Page 115
The optimal angle of tilt during calibration is
40 degrees
for the first four cardinal directions
(0, 90, 180, and 270) and
65 degrees
for the other eight calibration points.
The center of rotation for the twelve calibration points is around the transducer head (and
therefore the compass).
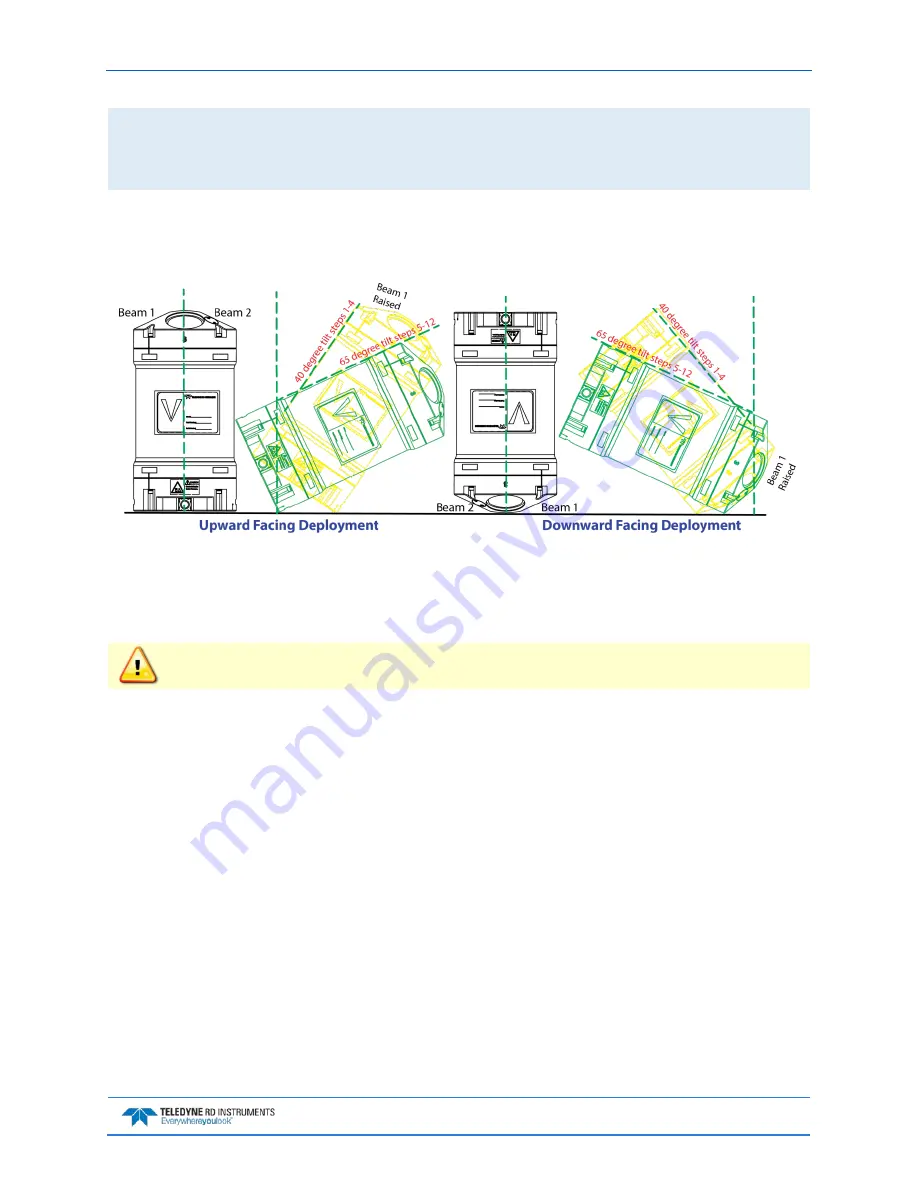
4. Place the ADCP on the Compass Calibration Guide in the same orientation as it will be deployed
(i.e. up or down) (see Figure 59). Each of the 12 steps has two parts: rotate the ADCP so that beam
1 is pointed toward the correct angle, and then tilt the ADCP 40 degrees for steps 1 through 4 and
65 degrees for steps 5 through 12.
Figure 59.
Upward or Downward Facing Deployment Hand-Held Compass Calibration
5. Hold the ADCP as still as possible at each step and click the Take sample button. The Sentinel V
checks for stability before it takes a calibration point. It should be held still in each position until
the point is taken.
There can be a delay in the acquisition of a calibration point after the Take sample button is
clicked. If the Sentinel V moved during the sample point, cancel the calibration and start over.
Overview of the 12 steps:
Step 1: You may rotate the ADCP in any direction. This direction will be your “0 degrees”.
Rotate ADCP so the Beam 1 points to 0
°
, Tilt the ADCP 40 degrees so that Beam 1 is up.
Click the Take sample button.
Step 2: Rotate the ADCP so the Beam 1 points to 90
°
, Tilt the ADCP 40 degrees so that Beam 2 is
up.
Click Take sample.
Step 3: Rotate the ADCP so the Beam 1 points to 180
°
, Tilt the ADCP 40 degrees so that Beam 1 is
up.
Click Take sample.
Step 4: Rotate the ADCP so the Beam 1 points to 270
°
, Tilt the ADCP 40 degrees so that Beam 2
is up.
Click Take sample.
Step 5: Rotate the ADCP so the Beam 1 points to 30
°
, Tilt the ADCP 65 degrees so that Beam 2
and Beam 4 are up.
Click Take sample.






























