CHAPTER 17 INTERRUPT/EXCEPTION PROCESSING FUNCTION
User’s Manual U16896EJ2V0UD
545
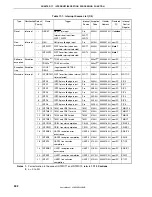
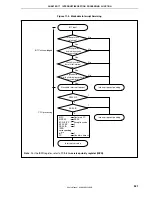
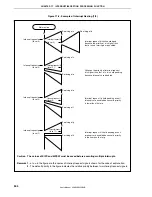
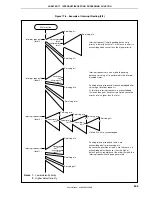
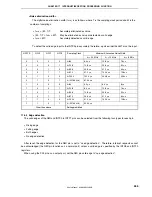
Figure 17-6. Example of Interrupt Nesting (2/2)
Main routine
EI
Interrupt request i
(level 2)
Servicing of i
Servicing of k
Interrupt request j
(level 3)
Servicing of j
Interrupt request l
(level 2)
EI
EI
EI
EI
Interrupt request o
(level 3)
Interrupt request s
(level 1)
Interrupt request k
(level 1)
Servicing of l
Servicing of n
Servicing of m
Servicing of s
Servicing of u
Servicing of t
Interrupt request m
(level 3)
Interrupt request n
(level 1)
Servicing of o
Interrupt request p
(level 2)
Interrupt request q
(level 1)
Interrupt request r
(level 0)
Interrupt request u
(level 2)
Note 2
Interrupt request t
(level 2)
Note 1
Servicing of p
Servicing of q
Servicing of r
EI
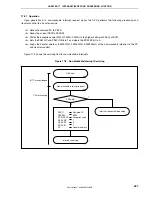
If levels 3 to 0 are acknowledged
Interrupt request j is held pending because its
priority is lower than that of i. k that occurs after j is
acknowledged because it has the higher priority.
Interrupt requests m and n are held pending
because servicing of l is performed in the interrupt
disabled status.
Pending interrupt requests are acknowledged after
servicing of interrupt request l.
At this time, interrupt request n is acknowledged
first even though m has occurred first because the
priority of n is higher than that of m.
Pending interrupt requests t and u are
acknowledged after processing of s.
Because the priorities of t and u are the same, u is
acknowledged first because it has the higher
default priority, regardless of the order in which the
interrupt requests have been generated.
Notes 1.
Lower default priority
2.
Higher default priority
Содержание ?PD703302
Страница 2: ...User s Manual U16896EJ2V0UD 2 MEMO ...