BASIC OPERATIONS
66
7.4.1. THEORETICAL ASPECTS OF THE REFLECTOMETRY
Main physical characteristics of the cable
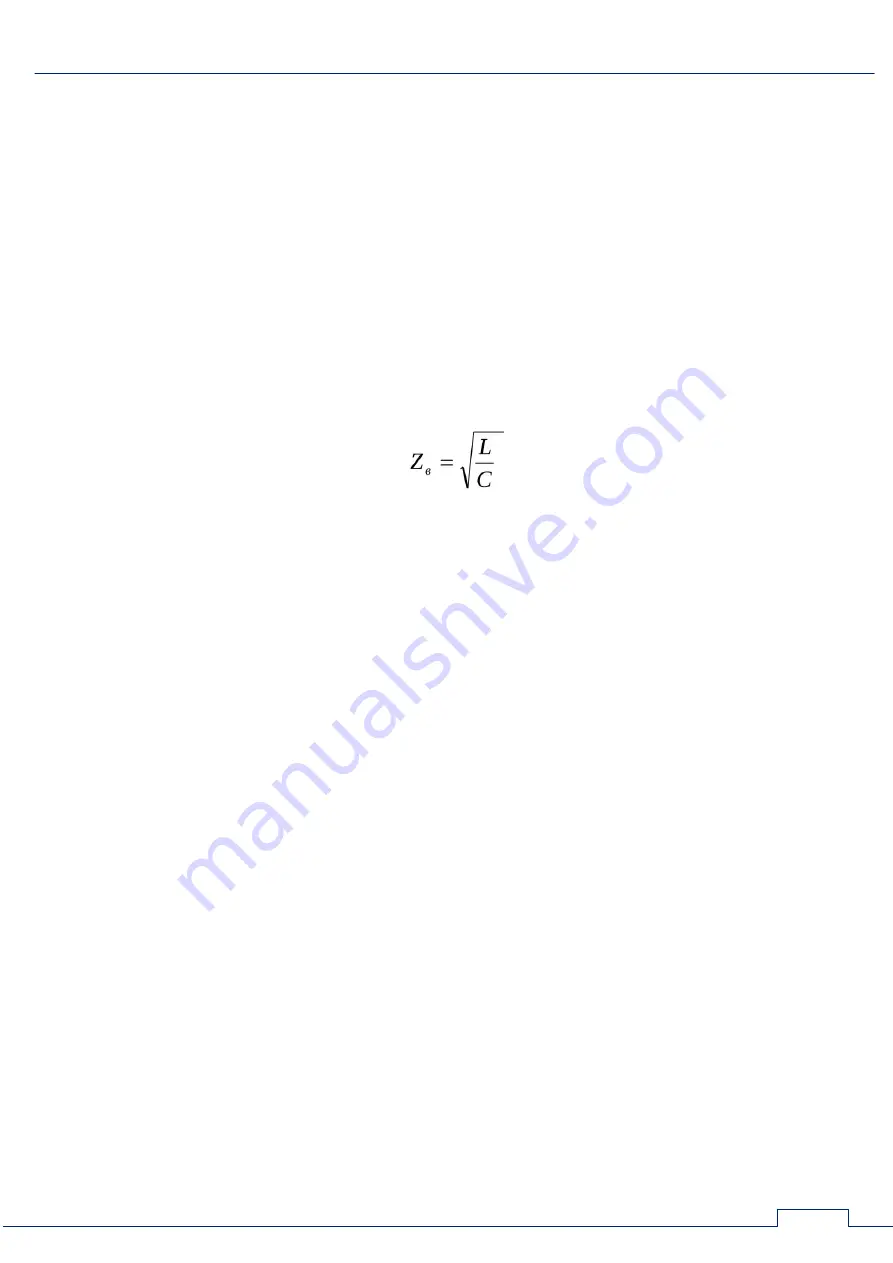
One of the characteristics of the cable is wave impedance (Z
b
), the resistance that an
electromagnetic wave encounters when propagating along any homogeneous (that is, without
reflection) guide system, including cable.
If the cable has no defects, its wave impedance does not change throughout. The only source
of reflected signal may be the end of the cable.
When testing all combinations of pairs of wires of such a cable, responses should be obtained
at the same distance corresponding to the length of the cable.
If there is a heterogeneity (break, short circuit or the devices connected to a cable) the
probing signal is reflected from it completely, or partially.
The wave impedance of the cable at high frequencies, which are usually used in pulse
reflectometers, is calculated by the formula:
Z
b
– wave impedance
L
– inductance
C – capacity
An increase in inductance leads to an increase in wave impedance, and an increase in
capacitance leads to its decrease.
The capacity of a two-wire line depends, inter alia, on the distance between the wires, which,
in this case, can be considered as plates of a capacitor.
The mutual arrangement of wires in a multi-wire cable will determine the wave impedance of
various combinations of wires. Increasing the distance between the two wires leads to a decrease
in capacitance and an increase in the value of wave impedance.
The wave impedance, which determines the attenuation of the signal, in different combinations
of wires of the same cable may be different.
Given that the level of the probing signal is the same for all tested wire combinations, it can be
assumed that the response levels in different combinations of such cables will not be the same.
In this case, certain patterns will appear that allow the correct interpretation of the test
results.
Relative positioning of wires in multi-wire low-current cables
The most common types of cables:
multi-wire round cable;
multi-wire flat cable;
multi-wire cable, consisting of several twisted pair.
Each type of a cable has features of a relative positioning of wires.
In multi-wire round cable,
the wires are approximately the same distance from each other.
The lengths of all wires are the same and match the length of the cable. The electrical parameters
(resistance, inductance, capacity) of all combinations of wires will be approximately the same.
















































