Quantum and Evolution Series Installation and Operating Handbook
8-49
Each packet passed to the modem must have this field set to the appropriate value in order
for the modem to recognize the different data streams.
8.12.9.5 Traffic Shaping Graphs
A web graphing facility exists that shows a line graph of throughput (in terms of bps) over
time for each QoS class. The data for each class is not superimposed, instead it is
necessary to select the particular class to be monitored graphically from a dropdown box. It
is easy to switch between graphs for the different classes in order to check that the level of
throughput is in line with expectations.
Graphs are time based and are shown in minute, hour, day and month formats. It is
intended to add diagnostic graphs per class in the future for errored packets and dropped
packets.
8.12.10 HTTP
Web
Acceleration
HTTP web acceleration speeds up the display of web pages.
Web pages are made up of multiple objects. Each in-line image is a separate object and
web browsers typically fetch each in-line object sequentially, one at a time, once the
skeleton web page has been received. Some browsers will start a second TCP
connection so two objects can be fetched in parallel. A typical web page with several
images can take multiple times the satellite delay before it is fully displayed.
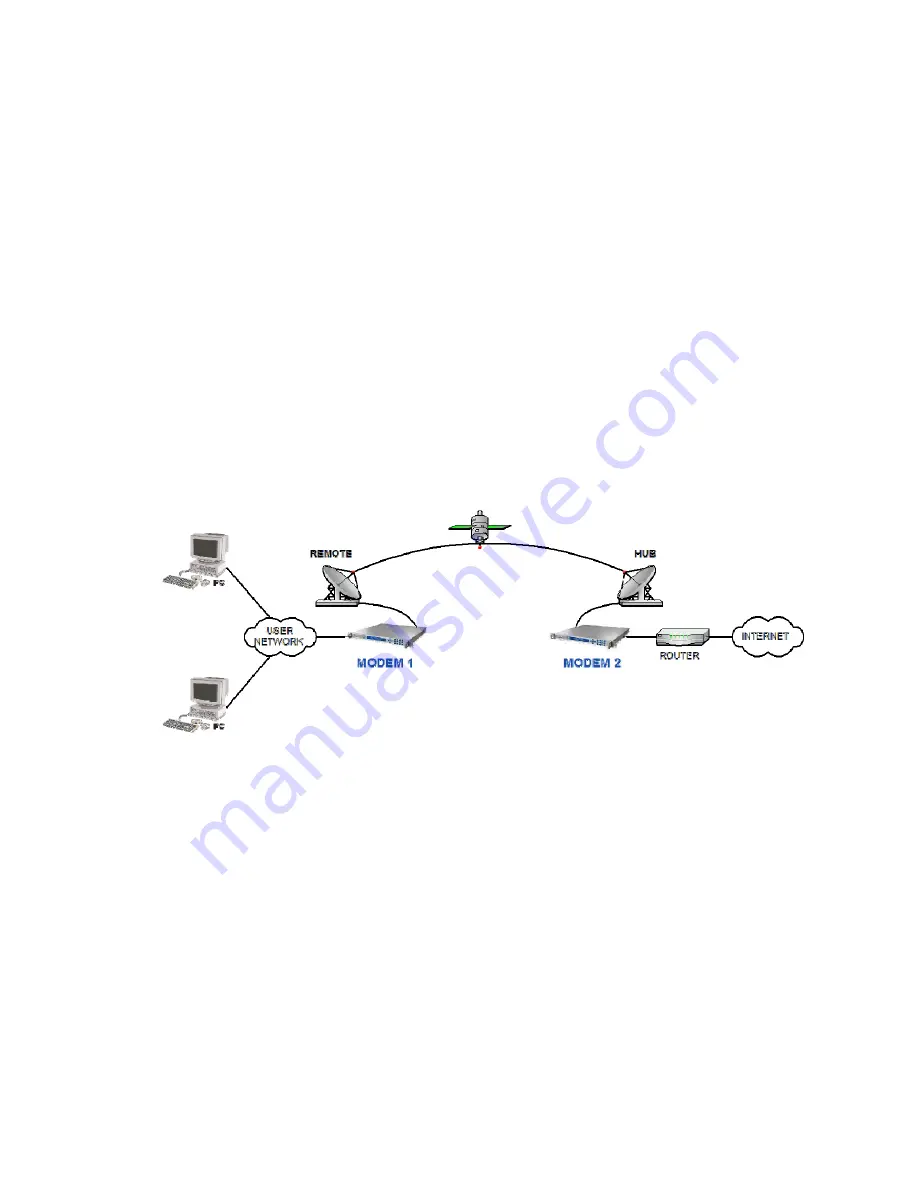
By prefetching all in-line objects in advance (in Modem 1 in the picture above), on
average there is a 30% reduction in the time taken to display a web page. Note that the
modem does not have enough memory to cache web pages – the benefit is due to
prefetching only.
The modem requires the IP address of a Domain Name Server (DNS) in order to convert
domain name requests into actual IP addresses.
HTTP web acceleration is provided as a free feature with TCP acceleration on the IP
Traffic card (it does not run on the base modem due to memory constraints).






























