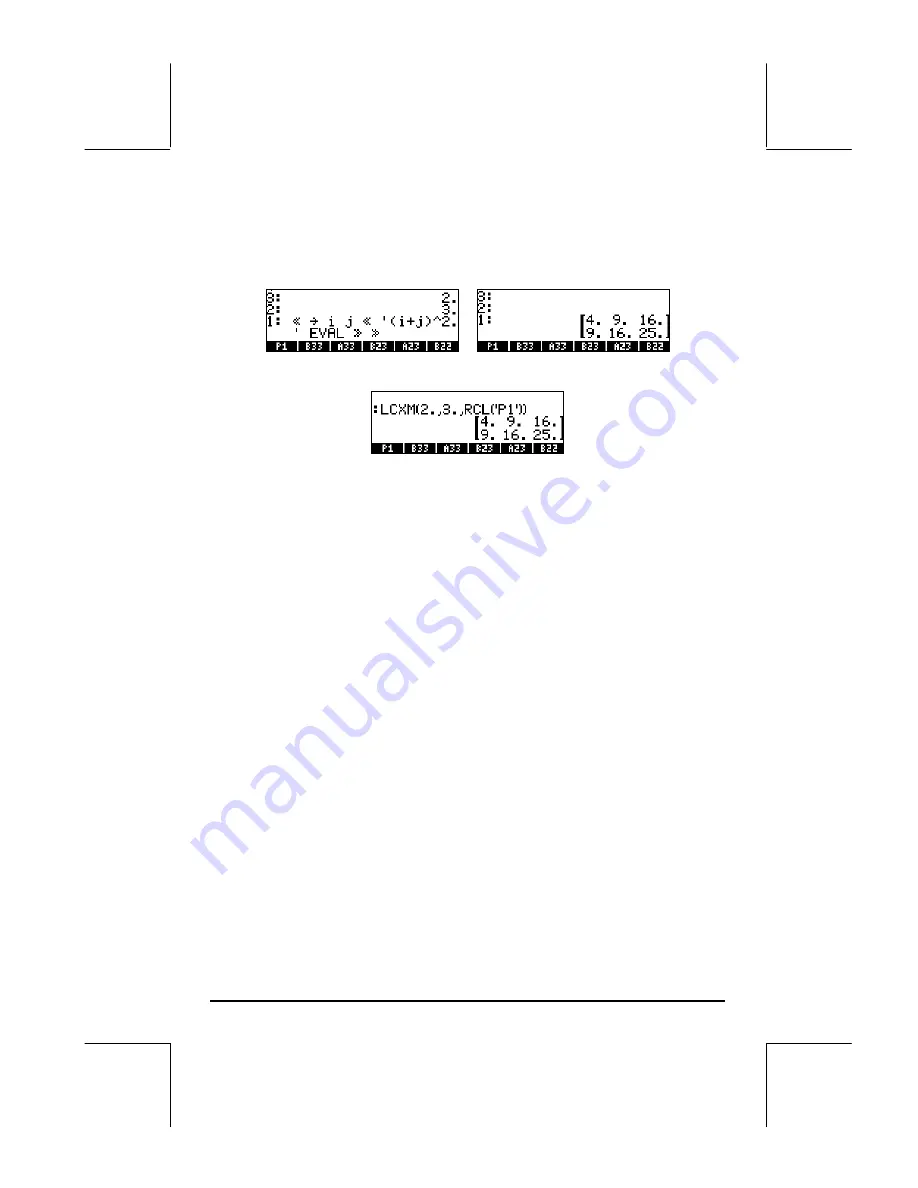
Page 11-16
The implementation of function LCXM for this case requires you to enter:
2`3`‚
@@P1@@
LCXM
`
The following figure shows the RPN stack before and after applying function
LCXM:
In ALG mode, this example can be obtained by using:
The program P1 must still have been created and stored in RPN mode.
Solution of linear systems
A system of
n
linear equations in
m
variables can be written as
a
11
⋅
x
1
+ a
12
⋅
x
2
+ a
13
⋅
x
3
+ …+ a
1,m-1
⋅
x
m-1
+ a
1,m
⋅
x
m
= b
1
,
a
21
⋅
x
1
+ a
22
⋅
x
2
+ a
23
⋅
x
3
+ …+ a
2,m-1
⋅
x
m-1
+ a
2,m
⋅
x
m
= b
2
,
a
31
⋅
x
1
+ a
32
⋅
x
2
+ a
33
⋅
x
3
+ …+ a
3,m-1
⋅
x
m-1
+ a
3,m
⋅
x
m
= b
3
,
. . . … . . .
. . . … . . .
a
n-1,1
⋅
x
1
+ a
n-1,2
⋅
x
2
+ a
n-1,3
⋅
x
3
+ …+ a
n-1,m-1
⋅
x
m-1
+ a
n-1,m
⋅
x
m
= b
n-1
,
a
n1
⋅
x
1
+ a
n2
⋅
x
2
+ a
n3
⋅
x
3
+ …+ a
n,m-1
⋅
x
m-1
+ a
n,m
⋅
x
m
= b
n
.
This system of linear equations can be written as a matrix equation,
A
n
×
m
⋅
x
m
×
1
=
b
n
×
1
, if we define the following matrix and vectors:
m
n
nm
n
n
m
m
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
A
×
=
L
M
O
M
M
L
L
2
1
2
22
21
1
12
11
,
1
2
1
×
=
m
m
x
x
x
x
M
,
1
2
1
×
=
n
n
b
b
b
b
M






























