Page 8-1
Chapter 8
Operations with lists
Lists are a type of calculator’s object that can be useful for data processing
and in programming. This Chapter presents examples of operations with lists.
Definitions
A list, within the context of the calculator, is a series of objects enclosed
between braces and separated by spaces (
#
), in the RPN mode, or
commas (
‚í
), in both modes. Objects that can be included in a list are
numbers, letters, character strings, variable names, and/or operators. Lists
are useful for manipulating data sets and in some programming applications.
Some examples of lists are:
{ t 1 }
,
{"BETA" h2 4}
,
{1 1.5 2.0}
,
{a a a a}
,
{ {1 2 3} {3 2 1} {1 2 3}}
In the examples shown below we will limit ourselves to numerical lists.
Creating and storing lists
To create a list in ALG mode, first enter the braces key
„ä
(associated
with the
+
key), then type or enter the elements of the list, separating them
with commas (
‚í
). The following keystrokes will enter the list {1 2 3 4}
and store it into variable L1.
„ä
1 ‚í 2
‚í 3
‚í 4
™K~l1`
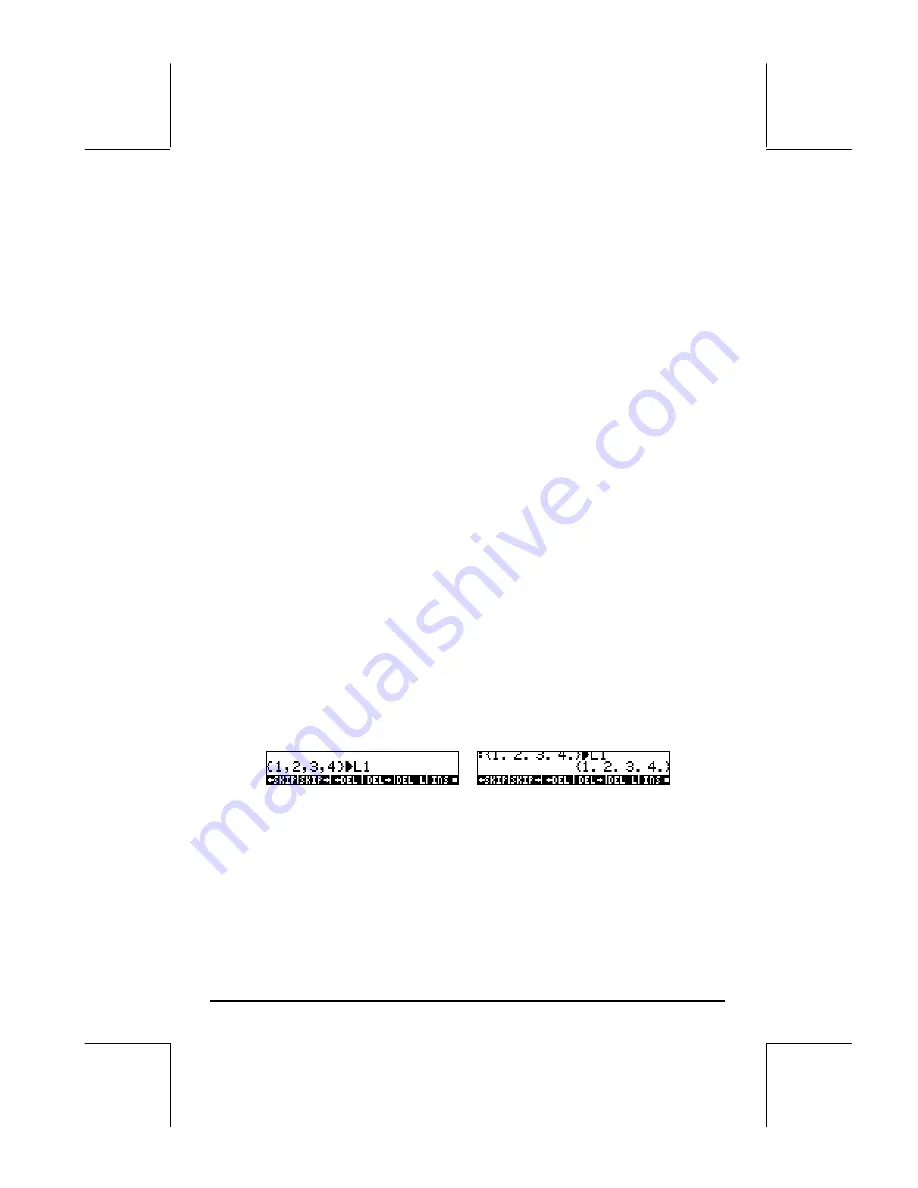
The screen will show the following:
The figure to the left shows the screen before pressing
`
, while the one to
the right shows the screen after storing the list into L1. Notice that before
pressing
`
the list shows the commas separating its elements. However,
after pressing
`
, the commas are replaced with spaces.
Entering the same list in RPN mode requires the following keystrokes:






























