Preliminary
S3C2451 RISC MICROPROCESSOR
UART
15-5
Preliminary product information describe products that are in development,
for which full characterization data and associated errata are not yet available.
Specifications and information herein are subject to change without notice.
RS-232C interface
If the user wants to connect the UART to modem interface (instead of null modem), nRTS, nCTS, nDSR, nDTR,
DCD and nRI signals are needed. In this case, the users can control these signals with general I/O ports by
software because the AFC does not support the RS-232C interface.
Interrupt/DMA Request Generation
Each UART of the S3C2451X has seven status (Tx/Rx/Error) signals: Overrun error, Parity error, Frame error,
Break, Receive buffer data ready, Transmit buffer empty, and Transmit shifter empty, all of which are indicated by
the corresponding UART status register (UTRSTATn/UERSTATn).
The overrun error, parity error, frame error and break condition are referred to as the receive error status. Each of
which can cause the receive error status interrupt request, if the receive-error-status-interrupt-enable bit is set to
one in the control register, UCONn. When a receive-error-status-interrupt-request is detected, the signal causing
the request can be identified by reading the value of UERSTSTn.
When the receiver transfers the data of the receive shifter to the receive FIFO register in FIFO mode and the
number of received data reaches Rx FIFO Trigger Level, Rx interrupt is generated. If the Receive mode is in
control register (UCONn) and is selected as 1 (Interrupt request or polling mode). In the Non-FIFO mode,
transferring the data of the receive shifter to receive holding register will cause Rx interrupt under the Interrupt
request and polling mode.
When the transmitter transfers data from its transmit FIFO register to its transmit shifter and the number of data
left in transmit FIFO reaches Tx FIFO Trigger Level, Tx interrupt is generated, if Transmit mode in control register
is selected as Interrupt request or polling mode. In the Non-FIFO mode, transferring data from the transmit
holding register to the transmit shifter will cause Tx interrupt under the Interrupt request and polling mode.
Note that the Tx interrupt is always requested whenever the number of data in the transmit FIFO is smaller than
the trigger level. This means that an interrupt is requested as soon as you enable the Tx interrupt unless you fill
the Tx buffer prior to that. It is recommended to fill the Tx buffer first and then enable the Tx interrupt.
If the Receive mode and Transmit mode in control register are selected as the DMAn request mode then DMAn
request occurs instead of Rx or Tx interrupt in the situation mentioned above.
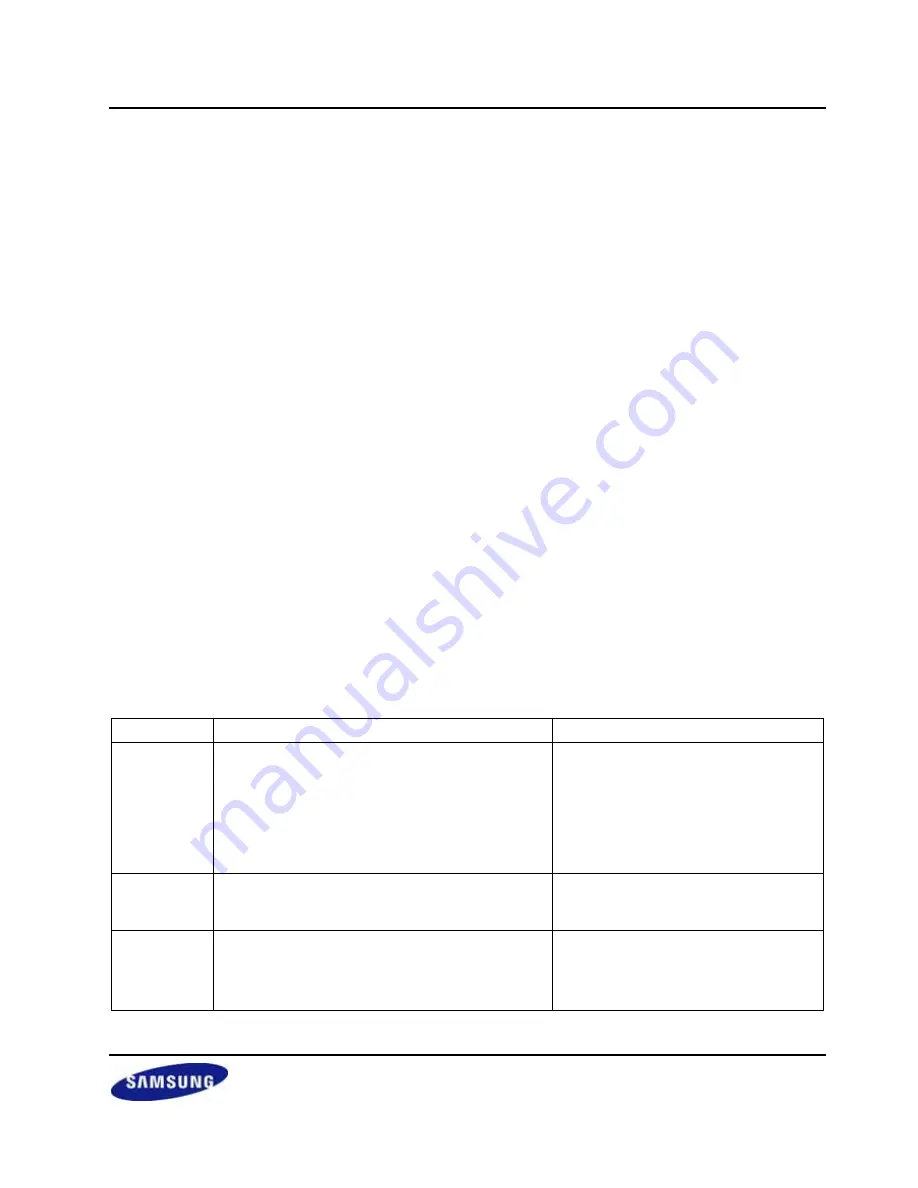
Table 15-1. Interrupts in Connection with FIFO
Type
FIFO Mode
Non-FIFO Mode
Rx Interrupt
Generated whenever receive data reaches the
trigger level of receive FIFO.
Generated when the number of data in FIFO does
not reaches Rx FIFO trigger Level and does not
receive any data during 3 words time (receive time
out). This interval follows the setting of Word Length
bit.
Generated by the receiving holding
register whenever receive buffer
becomes full.
Tx Interrupt
Generated whenever transmit data reaches the
trigger level of transmit FIFO (Tx FIFO trigger
Level).
Generated by the transmitting holding
register whenever transmit buffer
becomes empty.
Error Interrupt Generated when frame error, parity error, or break
signal are detected.
Generated when it gets to the top of the receive
FIFO without reading out data in it (overrun error).
Generated by all errors. However if
another error occurs at the same time,
only one interrupt is generated.















































