Digital Standard 3GPP W-CDMA (FDD)
SMIQ
1125.5555.03
E-9
2.172
I
Q
1
1
0
0
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
7
7
8
8
9
9
17
17
16
16
15
15
14
14
13
13
12
12
11
11
10
10
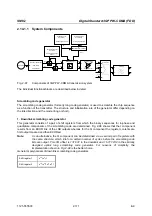
Fig. 2-98
Structure of the downlink scrambling code generator
The shift registers are initialized by loading shift register 1 with "0 to 01" and shift register 2 with all "1".
In addition, shift register 1 is run forward by n cycles, n being the scrambling code number or in short the
"scrambling code" (SC).
After a cycle time of one radio frame the generators are reset, i.e. the above initialization is carried out
again.
2. Uplink scrambling code generator
In the uplink, distinction is made between two modes of the SC. There is on the one hand the long SC
which can be used for all types of channel. On the other hand, there is the short SC which can be used
for all channels except PRACH and PCPCH as an alternative to the long SC.
a) Uplink long scrambling code generator
The code generator of the long SC in the uplink has basically the same structure as the SC in the
downlink. However, the generator polynomials of the shift registers and the type of initialization differ.
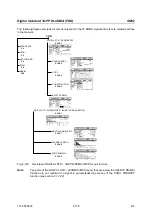
Table 2-19 Generator polynomials of uplink long scrambling code generators
Shift register 1
x
25
+x
3
+1
Shift register 2
x
25
+x
3
+x
2
+x+1
The shift registers are initialized by assigning 1 to bit number 24 in shift register 1 and the binary form of
the scrambling code number n to bits 23 to 0. Shift register 2 is loaded with all "1".
The readout positions for the Q component are such that they correspond to an IQ offset of 16.777.232
cycles.
After a cycle time of one radio frame the generators are reset, i.e. the above initialization is carried out
again.
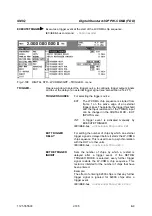
b) Uplink short scrambling code generator
The code generator of the short SC in the uplink comprises altogether 3 coupled shift registers.