| Authentication and Authorization |
301
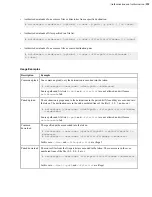
Because local storage objects are simple, you can create your access key by specifying the storage in
the command line:
# curl -ki -u nodeadmin:superP@55wOrD -X POST
https://localhost:9092/access_keys -d'{"storage":
{"type":"local","path":"/projects/project1"}}
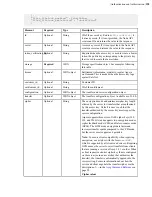
Amazon S3
{"storage" : {
"type" : "aws_s3",
"endpoint" : "s3.amazonaws.com",
"path" : "
bucket
/
path
/",
"storage_class" : "STANDARD|REDUCED_REDUNDANCY|
INFREQUENT_ACCESS",
"server_side_encryption" : "AES256|AWS_KMS",
"server_side_encryption_aws_kms_key_id" =
"
arn_encryption_key
",
"credentials" : {
"type" : "key|iam-role|assume-role",
"access_key_id" : "
aws_access_key
",
"secret_access_key" : "
secret_access_key
",
"iam_role_name" : "
iam_role
",
"assume_role_arn":
"arn:aws:iam::
your_aws_account_id
:role/
role_name
",
"assume_role_external_id" : "
external_id
",
"assume_role_session_name" : "
session_name
"
}
}}
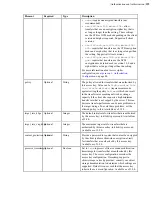
Where:
• "path" includes the bucket and file path.
• If server side encryption is set to
"AWS_KMS"
, then
"server_side_encryption_aws_kms_key_id"
is required and is set to the ARN of
the encryption key (for example,
"arn:aws:kms:us-east-1:648543846928:key/
er23525-8754-84g4-8sf7-4834ngigfre45"
).
• Values for credentials depend on the type of authentication you use. To authenticate with your
storage access key ID and secret, only specify "access_key_id" and "secret_access_key".
To authenticate with an IAM role, only specify "iam_role_name". To authenticate with
an assumed IAM role, only specify "assume_role_arn", "assume_role_external_id", and
"assume_role_session_name".
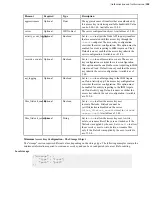
Azure (Block and Page Storage)
{"storage" : {
"type" : "azure",
"api" : "PAGE | BLOCK",
"container" : "
container
",
"path" : "
path
",
"credentials" : {
"storage_endpoint" : "blob.core.windows.net",
"type": "key",
"account" : "
account_name
",
"key" : "
storage_access_key
"
}
}}
Azure Data Lake Storage
"storage" : {