| ascp: Transferring from the Command Line with Ascp |
142
You can specify a transfer policy that determines how a FASP transfer utilizes the network resource, and you can
specify target and minimum transfer rates where applicable. In an
ascp
command, use the following flags to
specify transfer policies that are fixed, fair, high, or low:
Policy
Command template
Fixed
--policy=fixed -l
target_rate
Fair
--policy=fair -l
target_rate
-m
min_rate
High
--policy=high -l
target_rate
-m
min_rate
Low
--policy=low -l
target_rate
-m
min_rate
The policies have the following characteristics:
•
high
- Adjust the transfer rate to fully utilize the available bandwidth up to the maximum rate. When
congestion occurs, the transfer rate is twice as fast as a fair-policy transfer. The
high
policy requires
maximum (target) and minimum transfer rates.
•
fair
- Adjust the transfer rate to fully utilize the available bandwidth up to the maximum rate. When
congestion occurs, bandwidth is shared fairly by transferring at an even rate. The
fair
policy requires
maximum (target) and minimum transfer rates.
•
low
- Adjust the transfer rate to use the available bandwidth up to the maximum rate. Similar to fair mode, but
less aggressive when sharing bandwidth with other network traffic. When congestion occurs, the transfer rate
is reduced to the minimum rate until other traffic decreases.
•
fixed
- Attempt to transfer at the specified target rate, regardless of network or storage capacity. This can
decrease transfer performance and cause problems on the target storage. Aspera discourages using the
fixed
policy except in specific contexts, such as bandwidth testing. The
fixed
policy requires a maximum (target)
rate.
2. What transfer speed should I expect? How do I know if something is "wrong" with the speed?
Aspera's FASP transport has no theoretical throughput limit. Other than the network capacity, the transfer speed
may be limited by rate settings and resources of the computers. To verify that your system's FASP transfer can
fulfill the maximum bandwidth capacity, prepare a client computer to connect to a server, and test the maximum
bandwidth.
Note:
This test typically occupies most of a network's bandwidth. Aspera recommends this test be performed on a
dedicated file transfer line or during a time of low network activity.
On the client computer, start a transfer with fixed bandwidth policy. Start with a lower transfer rate and gradually
increase the transfer rate toward the network bandwidth (for example, 1 MB, 5 MB, 10 MB, and so on). Monitor
the transfer rate; at its maximum, it should be slightly below your available bandwidth:
$ ascp -l 1m
source-file destination
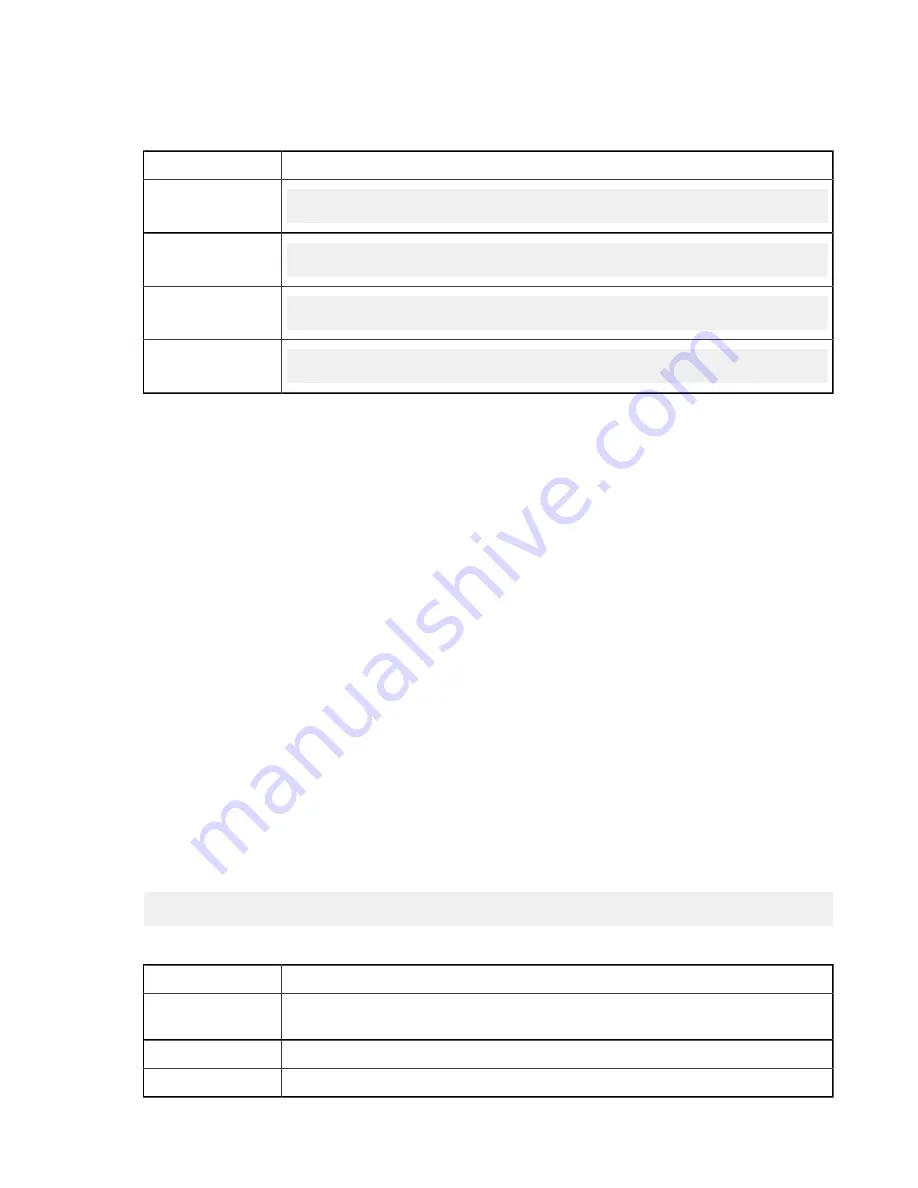
To improve the transfer speed, also consider upgrading the following hardware components:
Component
Description
Hard disk
The I/O throughput, the disk bus architecture (such as RAID, IDE, SCSI, ATA, and Fiber
Channel).
Network I/O
The interface card, the internal bus of the computer.
CPU
Overall CPU performance affects the transfer, especially when encryption is enabled.